CobB regulates Escherichia coli chemotaxis by deacetylating the response regulator CheY
- PMID: 20345663
- PMCID: PMC2883070
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07125.x
CobB regulates Escherichia coli chemotaxis by deacetylating the response regulator CheY
Abstract
The silent information regulator (Sir2) family proteins are NAD+-dependent deacetylases. Although a few substrates have been identified, functions of the bacteria Sir2-like protein (CobB) still remain unclear. Here the role of CobB on Escherichia coli chemotaxis was investigated. We used Western blotting and mass spectrometry to show that the response regulator CheY is a substrate of CobB. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) indicated that acetylation affects the interaction between CheY and the flagellar switch protein FliM. The presence of intact flagella in knockout strains DeltacobB, Deltaacs, Delta(cobB) Delta(acs), Delta(cheA) Delta(cheZ), Delta(cheA) Delta(cheZ) Delta(cobB) and Delta(cheA) Delta(cheZ) Delta(acs) was confirmed by electron microscopy. Genetic analysis of these knockout strains showed that: (i) the DeltacobB mutant exhibited reduced responses to chemotactic stimuli in chemotactic assays, whereas the Deltaacs mutant was indistinguishable from the parental strain, (ii) CheY from the DeltacobB mutant showed a higher level of acetylation, indicating that CobB can mediate the deacetylation of CheY in vivo, and (iii) deletion of cobB reversed the phenotype of Delta(cheA) Delta(cheZ). Our findings suggest that CobB regulates E. coli chemotaxis by deacetylating CheY. Thus a new function of bacterial cobB was identified and also new insights of regulation of bacterial chemotaxis were provided.
Figures
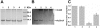
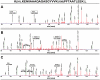
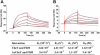
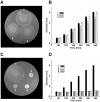
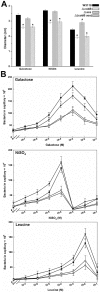
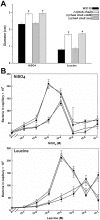
 ) W3110 Δ(cheA) Δ(cheZ) mutant; (▿) W3110 Δ(cheA) Δ(cheZ) Δ(cobB) mutant; (◊) W3110 Δ(cheA) Δ(cheZ) Δ(acs) mutant.
) W3110 Δ(cheA) Δ(cheZ) mutant; (▿) W3110 Δ(cheA) Δ(cheZ) Δ(cobB) mutant; (◊) W3110 Δ(cheA) Δ(cheZ) Δ(acs) mutant.Similar articles
-
The chemotaxis response regulator CheY can catalyze its own acetylation.J Mol Biol. 2006 Jun 2;359(2):251-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.03.033. Epub 2006 Mar 31. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16630631
-
Co-regulation of acetylation and phosphorylation of CheY, a response regulator in chemotaxis of Escherichia coli.J Mol Biol. 2004 Sep 10;342(2):375-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.021. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15327941
-
Acetylation represses the binding of CheY to its _target proteins.Mol Microbiol. 2010 May;76(4):932-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07148.x. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20398208
-
pH sensing in bacterial chemotaxis.Novartis Found Symp. 1999;221:38-50; discussions 50-4. doi: 10.1002/9780470515631.ch4. Novartis Found Symp. 1999. PMID: 10207912 Review.
-
Response regulation in bacterial chemotaxis.J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jan;51(1):41-6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510109. J Cell Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8381790 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Sirtuins Overview: An Open Niche to Explore.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 26;12:744416. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.744416. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34803965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methylation of PhoP by CheR Regulates Salmonella Virulence.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0209921. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02099-21. Epub 2021 Sep 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34544273 Free PMC article.
-
The switching mechanism of the bacterial rotary motor combines tight regulation with inherent flexibility.EMBO J. 2021 Mar 15;40(6):e104683. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104683. Epub 2021 Feb 23. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 33620739 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible lysine acetylation is involved in DNA replication initiation by regulating activities of initiator DnaA in Escherichia coli.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 3;6:30837. doi: 10.1038/srep30837. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27484197 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Acetylation and Butyrylation Regulate the Phenotype and Metabolic Shifts of the Endospore-forming Clostridium acetobutylicum.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018 Jun;17(6):1156-1169. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA117.000372. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29523768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science. 1966;153:708–716. - PubMed
-
- Baker MD, Wolanin PM, Stock JB. Signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Bioessays. 2006;28:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Barak R, Eisenbach M. Acetylation of the response regulator, CheY, is involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Mol Microbiol. 2001;40:731–743. - PubMed
-
- Barak R, Eisenbach M. Co-regulation of acetylation and phosphorylation of CheY, a response regulator in chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 2004;342:375–381. - PubMed
-
- Barak R, Welch M, Yanovsky A, Oosawa K, Eisenbach M. Acetyladenylate or its derivative acetylates the chemotaxis protein CheY in vitro and increases its activity at the flagellar switch. Biochemistry. 1992;31:10099–10107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

