A high-throughput respirometric assay for mitochondrial biogenesis and toxicity
- PMID: 20465991
- PMCID: PMC2900494
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.04.040
A high-throughput respirometric assay for mitochondrial biogenesis and toxicity
Abstract
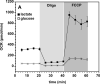
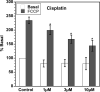
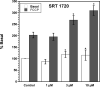
Mitochondria are a common _target of toxicity for drugs and other chemicals and result in decreased aerobic metabolism and cell death. In contrast, mitochondrial biogenesis restores cell vitality, and there is a need for new agents to induce biogenesis. Current cell-based models of mitochondrial biogenesis or toxicity are inadequate because cultured cell lines are highly glycolytic with minimal aerobic metabolism and altered mitochondrial physiology. In addition, there are no high-throughput real-time assays that assess mitochondrial function. We adapted primary cultures of renal proximal tubular cells (RPTCs) that exhibit in vivo levels of aerobic metabolism, are not glycolytic, and retain higher levels of differentiated functions and used the Seahorse Bioscience analyzer to measure mitochondrial function in real time in multiwell plates. Using uncoupled respiration as a marker of electron transport chain (ETC) integrity, the nephrotoxicants cisplatin, HgCl(2), and gentamicin exhibited mitochondrial toxicity prior to decreases in basal respiration and cell death. Conversely, using FCCP (carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone)-uncoupled respiration as a marker of maximal ETC activity, 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI), SRT1720, resveratrol, daidzein, and metformin produced mitochondrial biogenesis in RPTCs. The merger of the RPTC model and multiwell respirometry results in a single high-throughput assay to measure mitochondrial biogenesis and toxicity and nephrotoxic potential.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures












Similar articles
-
The β2-adrenoceptor agonist formoterol stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Jul;342(1):106-18. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.191528. Epub 2012 Apr 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22490378 Free PMC article.
-
SRT1720 induces mitochondrial biogenesis and rescues mitochondrial function after oxidant injury in renal proximal tubule cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 May;333(2):593-601. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.161992. Epub 2010 Jan 26. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20103585 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput respirometric assay identifies predictive toxicophore of mitochondrial injury.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;272(2):490-502. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23811330 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput assessment of oxidative respiration in fish embryos: Advancing adverse outcome pathways for mitochondrial dysfunction.Aquat Toxicol. 2018 Jun;199:162-173. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.03.031. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Aquat Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29631217 Review.
-
A novel high-throughput assay for respiration in isolated brain microvessels reveals impaired mitochondrial function in the aged mice.Geroscience. 2018 Aug;40(4):365-375. doi: 10.1007/s11357-018-0037-8. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Geroscience. 2018. PMID: 30074132 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SRT1720 improves survival and healthspan of obese mice.Sci Rep. 2011;1:70. doi: 10.1038/srep00070. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Sci Rep. 2011. PMID: 22355589 Free PMC article.
-
5-hydroxytryptamine 1F Receptor Agonist Induces Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Promotes Recovery from Spinal Cord Injury.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020 Feb;372(2):216-223. doi: 10.1124/jpet.119.262410. Epub 2019 Nov 27. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020. PMID: 31776207 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Drug-Induced Mitochondrial Toxicity in Cardiomyocytes: Implications for Preclinical Cardiac Safety Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 21;14(7):1313. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071313. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-HT1F receptor agonism induces mitochondrial biogenesis and increases cellular function in brain microvascular endothelial cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Mar 5;18:1365158. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1365158. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38510106 Free PMC article.
-
LCL124, a cationic analog of ceramide, selectively induces pancreatic cancer cell death by accumulating in mitochondria.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Jan;344(1):167-78. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.199216. Epub 2012 Oct 18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23086228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dekant W. Biotransformation and renal processing of nephrotoxic agents. Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 1996;18:163–72. - PubMed
-
- Hall AM, Unwin RJ. The not so ‘mighty chondrion’: emergence of renal diseases due to mitochondrial dysfunction. Nephron. Physiol. 2007;105:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Rasbach KA, Schnellmann RG. Signaling of mitochondrial biogenesis following oxidant injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:2355–62. - PubMed
-
- Rasbach KA, Schnellmann RG. PGC-1alpha over-expression promotes recovery from mitochondrial dysfunction and cell injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007;13:734–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

