Genetic basis of Candida biofilm resistance due to drug-sequestering matrix glucan
- PMID: 20497051
- PMCID: PMC2880631
- DOI: 10.1086/651200
Genetic basis of Candida biofilm resistance due to drug-sequestering matrix glucan
Abstract
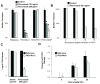
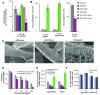
Medical devices provide an ecological niche for microbes to flourish as a biofilm community, protected from antimicrobials and host defenses. Biofilms formed by Candida albicans, the most common fungal pathogen, survive exposure to extraordinarily high drug concentrations. Here, we show that beta-glucan synthase Fks1p produces glucan, which is deposited in the biofilm matrix. The extracellular glucan is required for biofilm resistance and acts by sequestering antifungals, rendering cells resistant to their action. These findings provide the genetic basis for how biofilm matrix production governs drug resistance by impeding drug diffusion and also identify a useful biofilm drug _target.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: J. N. No conflict, H. S. No conflict, M.C. No conflict, D. A. No conflict
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interface of Candida albicans biofilm matrix-associated drug resistance and cell wall integrity regulation.Eukaryot Cell. 2011 Dec;10(12):1660-9. doi: 10.1128/EC.05126-11. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Eukaryot Cell. 2011. PMID: 21666076 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Fks1p and matrix glucan in Candida albicans biofilm resistance to an echinocandin, pyrimidine, and polyene.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Aug;54(8):3505-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00227-10. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20516280 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Candida albicans biofilms with antifungals: transcriptional response and binding of antifungals to beta-glucans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 May;54(5):2096-111. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01638-09. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20194705 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of biomaterials and antifungals on biofilm formation by Candida species: a review.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012 Oct;31(10):2513-27. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1634-6. Epub 2012 May 12. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22581304 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Candida biofilm drug resistance.Future Microbiol. 2013 Oct;8(10):1325-37. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.101. Future Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24059922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An expanded regulatory network temporally controls Candida albicans biofilm formation.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Jun;96(6):1226-39. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13002. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25784162 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroquine sensitizes biofilms of Candida albicans to antifungal azoles.Braz J Infect Dis. 2013 Jul-Aug;17(4):395-400. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2012.11.002. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Braz J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23602464 Free PMC article.
-
Interface of Candida albicans biofilm matrix-associated drug resistance and cell wall integrity regulation.Eukaryot Cell. 2011 Dec;10(12):1660-9. doi: 10.1128/EC.05126-11. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Eukaryot Cell. 2011. PMID: 21666076 Free PMC article.
-
Candida Species Biofilms' Antifungal Resistance.J Fungi (Basel). 2017 Feb 21;3(1):8. doi: 10.3390/jof3010008. J Fungi (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29371527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and regulation of single- and multi-species Candida albicans biofilms.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018 Jan;16(1):19-31. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.107. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29062072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gola S, Martin R, Walther A, Dunkler A, Wendland J. New modules for PCR-based gene _targeting in Candida albicans: rapid and efficient gene _targeting using 100 bp of flanking homology region. Yeast. 2003;20:1339–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

