Molecular signature of mineralocorticoid receptor signaling in cardiomyocytes: from cultured cells to mouse heart
- PMID: 20591974
- PMCID: PMC2940498
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-0237
Molecular signature of mineralocorticoid receptor signaling in cardiomyocytes: from cultured cells to mouse heart
Abstract
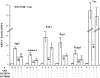
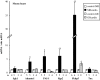
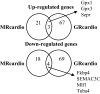
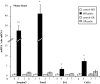
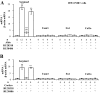
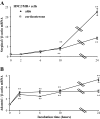
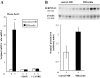
Excess mineralocorticoid signaling is deleterious for cardiovascular functions, as demonstrated by the beneficial effects of mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonism on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure. However, the understanding of signaling pathways after MR activation in the heart remains limited. We performed transcriptomic analyses in the heart of double-transgenic mice with conditional, cardiomyocyte-specific, overexpression of the MR (MRcardio mice) or the glucocorticoid receptor (GR; GRcardio mice). Some of the genes induced in MRcardio mice were selected for comparative evaluation (real time PCR) in vivo in the heart of mice and ex vivo in the MR-expressing cardiomyocyte H9C2 cell line after aldosterone or corticosterone treatment. We demonstrate that chronic MR overexpression in the heart results in a limited number of induced (n = 24) and repressed (n = 22) genes compared with their control littermates. These genes are specifically modulated by MR because there is limited overlap (three induced, four repressed) with the genes that are regulated in the heart of GRcardio mice (compared with control mice: 70 induced, 73 repressed). Interestingly, some MR-induced genes that are up-regulated in vivo in mice are also induced by 24-h aldosterone treatment in H9C2 cells, such as plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and Serpina-3 (alpha1-antichymotrypsin). The signaling pathways that are affected by long-term activation of MR may be of particular interest to design novel therapeutic _targets in cardiac diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The diuretic torasemide does not prevent aldosterone-mediated mineralocorticoid receptor activation in cardiomyocytes.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 9;8(9):e73737. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073737. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040049 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone-specific activation of cardiomyocyte mineralocorticoid receptor in vivo.Hypertension. 2013 Feb;61(2):361-7. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.198986. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23297371
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a novel mineralocorticoid _target in the cardiovascular system.Hypertension. 2012 May;59(5):966-72. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.187872. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Hypertension. 2012. PMID: 22469622
-
Glucocorticoid signaling in the heart: A cardiomyocyte perspective.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Sep;153:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Mar 21. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25804222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac GR and MR: From Development to Pathology.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jan;27(1):35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26586027 Review.
Cited by
-
Antagonistic Roles of GRK2 and GRK5 in Cardiac Aldosterone Signaling Reveal GRK5-Mediated Cardioprotection via Mineralocorticoid Receptor Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 20;21(8):2868. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082868. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326036 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyocyte glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors directly and antagonistically regulate heart disease in mice.Sci Signal. 2019 Apr 16;12(577):eaau9685. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aau9685. Sci Signal. 2019. PMID: 30992401 Free PMC article.
-
CMR-Verified Myocardial Fibrosis Is Associated With Subclinical Diastolic Dysfunction in Primary Aldosteronism Patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 14;12:672557. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.672557. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34054733 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone and cardiovascular disease: the heart of the matter.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jan;24(1):21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23040074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The decrease of mineralcorticoid receptor drives angiogenic pathways in colorectal cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59410. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059410. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Young M, Funder JW 2000 Aldosterone and the heart. Trends Endocrinol Metab 11:224–226 - PubMed
-
- Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A, Palensky J, Wittes J 1999 The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 341:709–717 - PubMed
-
- Pitt B, Remme W, Zannad F, Neaton J, Martinez F, Roniker B, Bittman R, Hurley S, Kleiman J, Gatlin M 2003 Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 348:1309–1321 - PubMed
-
- Fuller PJ, Young MJ 2005 Mechanisms of mineralocorticoid action. Hypertension 46:1227–1235 - PubMed
-
- Farman N, Rafestin-Oblin ME 2001 Multiple aspects of mineralocorticoid selectivity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F181–F192 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

