PTEN, PIK3CA, p-AKT, and p-p70S6K status: association with trastuzumab response and survival in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 20813970
- PMCID: PMC2947262
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090885
PTEN, PIK3CA, p-AKT, and p-p70S6K status: association with trastuzumab response and survival in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
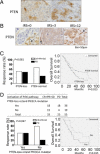
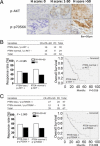
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a key modulator of trastuzumab sensitivity in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Because PTEN opposes the downstream signaling of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), we investigated the role of PTEN and other components of the PI3K pathway in trastuzumab resistance. We analyzed the status of PTEN, p-AKT-Ser473, and p-p70S6K-Thr389 using immunohistochemistry. PIK3CA mutation status was analyzed by direct sequencing. Primary tumor tissue was available from 137 patients with HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer who had received trastuzumab-based chemotherapy. We observed that each of the four biomarkers alone did not significantly correlate with trastuzumab response, whereas PTEN loss alone significantly correlated with shorter survival times (P = 0.023). PI3K pathway activation, defined as PTEN loss and/or PIK3CA mutation, was associated with a poor response to trastuzumab (P = 0.047) and a shorter survival time (P = 0.015). PTEN loss was significantly associated with a poor response to trastuzumab (P = 0.028) and shorter survival time (P = 0.008) in patients who had received first-line trastuzumab and in patients with estrogen receptor- (P = 0.029) and progesterone receptor-negative tumors (P = 0.033). p-AKT-Ser473 and p-p70S6K-Thr389 each had a limited correlation with trastuzumab response. When these markers were combined with PTEN loss, an increased correlation with patient outcome was observed. In conclusion, PI3K pathway activation plays a pivotal role in trastuzumab resistance. Our findings may facilitate the evaluation of tumor response to trastuzumab-based and _targeted therapies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the association of PIK3CA mutations and PTEN loss with efficacy of trastuzumab therapy in metastatic breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Jul;128(2):447-56. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1572-5. Epub 2011 May 19. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21594665
-
Frequent mutational activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Dec 15;18(24):6784-91. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1785. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23092874 Free PMC article.
-
Increased signalling of EGFR and IGF1R, and deregulation of PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway are related with trastuzumab resistance in HER2 breast carcinomas.Br J Cancer. 2012 Apr 10;106(8):1367-73. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.85. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22454081 Free PMC article.
-
[Trastuzumab (Herceptin) and breast cancer: mechanisms of resistance].Bull Cancer. 2007 Mar;94(3):259-66. Bull Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17371768 Review. French.
-
Evolving strategies for overcoming resistance to HER2-directed therapy: _targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.Clin Breast Cancer. 2010 Nov;10 Suppl 3:S72-8. doi: 10.3816/CBC.2010.s.015. Clin Breast Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21115425 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of antibody that inhibits ligand-independent HER3 dimerization and a p110α inhibitor potently blocks PI3K signaling and growth of HER2+ breast cancers.Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 1;73(19):6013-23. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1191. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23918797 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Underlying the Action and Synergism of Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab in _targeting HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Sep 20;10(10):342. doi: 10.3390/cancers10100342. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30241301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HER2-amplified breast cancer: mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance and novel _targeted therapies.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011 Feb;11(2):263-75. doi: 10.1586/era.10.226. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21342044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERBB receptors: from oncogene discovery to basic science to mechanism-based cancer therapeutics.Cancer Cell. 2014 Mar 17;25(3):282-303. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.02.025. Cancer Cell. 2014. PMID: 24651011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The unpluggable in pursuit of the undruggable: tackling the dark matter of the cancer therapeutics universe.Front Oncol. 2013 Dec 12;3:304. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00304. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24377088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Rohan TE, Hartwick W, Miller AB, Kandel RA. Immunohistochemical detection of c-erbB-2 and p53 in benign breast disease and breast cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:1262–1269. - PubMed
-
- Hynes NE, MacDonald G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:177–184. - PubMed
-
- Kurokawa H, Arteaga CL. ErbB (HER) receptors can abrogate antiestrogen action in human breast cancer by multiple signaling mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:511S–515S. - PubMed
-
- Emens LA. Trastuzumab: _targeted therapy for the management of HER-2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Am J Ther. 2005;12:243–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

