PGC-1 coactivators in cardiac development and disease
- PMID: 20884884
- PMCID: PMC2955978
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223818
PGC-1 coactivators in cardiac development and disease
Abstract
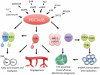
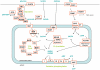
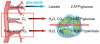
The beating heart requires a constant flux of ATP to maintain contractile function, and there is increasing evidence that energetic defects contribute to the development of heart failure. The last 10 years have seen a resurgent interest in cardiac intermediary metabolism and a dramatic increase in our understanding of transcriptional networks that regulate cardiac energetics. The PPAR-γ coactivator (PGC)-1 family of proteins plays a central role in these pathways. The mechanisms by which PGC-1 proteins regulate transcriptional networks and are regulated by physiological cues, as well as the roles they play in cardiac development and disease, are reviewed here.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PGC-1 proteins and heart failure.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2012 May;22(4):98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2012. PMID: 22939990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-alpha (PPARα) and PPAR gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1α) regulation of cardiac metabolism in diabetes.Pediatr Cardiol. 2011 Mar;32(3):323-8. doi: 10.1007/s00246-011-9889-8. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Pediatr Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21286700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators, energy homeostasis, and metabolism.Endocr Rev. 2006 Dec;27(7):728-35. doi: 10.1210/er.2006-0037. Epub 2006 Oct 3. Endocr Rev. 2006. PMID: 17018837 Review.
-
PGC-1 coactivators in the control of energy metabolism.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011 Apr;43(4):248-57. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmr007. Epub 2011 Feb 16. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011. PMID: 21325336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bcl3 interacts cooperatively with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) coactivator 1alpha to coactivate nuclear receptors estrogen-related receptor alpha and PPARalpha.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Aug;29(15):4091-102. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01669-08. Epub 2009 May 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19451226 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PGC1/PPAR drive cardiomyocyte maturation at single cell level via YAP1 and SF3B2.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 12;12(1):1648. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21957-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33712605 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor Tfe3 Directly Regulates Pgc-1alpha in Muscle.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Oct;230(10):2330-6. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24978. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25736533 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic caloric restriction attenuates a loss of sulfatide content in PGC-1α-/- mouse cortex: a potential lipidomic role of PGC-1α in neurodegeneration.J Lipid Res. 2012 Feb;53(2):273-81. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M020628. Epub 2011 Nov 23. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22114039 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle-packaged mitochondrial disturbing miRNA exacerbates cardiac injury during acute myocardial infarction.Clin Transl Med. 2022 Apr;12(4):e779. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.779. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35452193 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiotoxicity with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor therapy.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2018 May 8;2:13. doi: 10.1038/s41698-018-0056-z. eCollection 2018. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30202791 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lopaschuk GD, Spafford MA. Energy substrate utilization by isolated working hearts from newborn rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1990;258:H1274–1280. - PubMed
-
- Lopaschuk GD, Collins-Nakai RL, Itoi T. Developmental changes in energy substrate use by the heart. Cardiovasc Res. 1992;26:1172–1180. - PubMed
-
- Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R, Wright M, Spiegelman BM. A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell. 1998;92:829–839. - PubMed
-
- Lin J, Handschin C, Spiegelman BM. Metabolic control through the pgc-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005;1:361–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

