APC/C-Cdh1: from cell cycle to cellular differentiation and genomic integrity
- PMID: 20935501
- PMCID: PMC3047751
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.19.13585
APC/C-Cdh1: from cell cycle to cellular differentiation and genomic integrity
Abstract
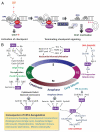
Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is a multifunctional ubiquitin-protein ligase that _targets various substrates for proteolysis inside and outside of the cell cycle. The activation of APC/C is dependent on two WD-40 domain proteins, Cdc20 and Cdh1. While APC/Cdc20 principally regulates mitotic progression, APC/Cdh1 shows a broad spectrum of substrates in and beyond cell cycle. In the past several years, numerous biochemical and mouse genetic studies have greatly attracted our attention to the emerging role of APC/Cdh1 in genomic integrity, cellular differentiation and human diseases. This review will aim to summarize the recently expanded understanding of APC/Cdh1 in regulating biological function and how its dysfunction may lead to diseases.
Figures

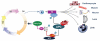
Similar articles
-
The emerging role of APC/CCdh1 in development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Aug;22(6):579-85. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.03.012. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21497201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic regulation of the anaphase-promoting complex.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Mar;64(5):589-600. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-6443-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17334950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of Cdc20 proteolysis reveals a role for APC components Cdc23 and Cdc27 during S phase and early mitosis.Curr Biol. 1998 Jun 18;8(13):750-60. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70298-2. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9651679
-
TPR subunits of the anaphase-promoting complex mediate binding to the activator protein CDH1.Curr Biol. 2003 Sep 2;13(17):1459-68. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00581-5. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12956947
-
Modulation of the mitotic regulatory network by APC-dependent destruction of the Cdh1 inhibitor Acm1.Mol Cell. 2008 May 23;30(4):437-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.04.004. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18498748 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cdc20: a potential novel therapeutic _target for cancer treatment.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(18):3210-4. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319180005. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23151139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient terminal erythroid differentiation requires the APC/C cofactor Cdh1 to limit replicative stress in erythroblasts.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 21;12(1):10489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14331-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35729193 Free PMC article.
-
APC-Cdh1 Inhibits the Proliferation and Activation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells after Mechanical Stretch Injury.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 17;2019:9524561. doi: 10.1155/2019/9524561. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31139661 Free PMC article.
-
NEK7 is required for G1 progression and procentriole formation.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Jul 15;28(15):2123-2134. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-09-0643. Epub 2017 May 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28539406 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of APC/CCdh1 in development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Aug;22(6):579-85. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.03.012. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21497201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peters JM. The anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome: a machine designed to destroy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:2–4. - PubMed
-
- Visintin R, Prinz S, Amon A. CDC20 and CDH1: A family of substrate-specific activators of APC-dependent proteolysis. Science. 1997;278:460–463. - PubMed
-
- Fang G, Yu H, Kirschner MW. Direct binding of CDC20 protein family members activates the anaphase-promoting complex in mitosis and G1. Mol Cell. 1998;2:163–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
