Pharmacologic inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex induces a spindle checkpoint-dependent mitotic arrest in the absence of spindle damage
- PMID: 20951947
- PMCID: PMC2957475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.08.010
Pharmacologic inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex induces a spindle checkpoint-dependent mitotic arrest in the absence of spindle damage
Abstract
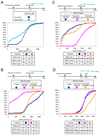
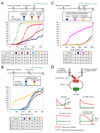
Microtubule inhibitors are important cancer drugs that induce mitotic arrest by activating the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), which, in turn, inhibits the ubiquitin ligase activity of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC). Here, we report a small molecule, tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester (TAME), which binds to the APC and prevents its activation by Cdc20 and Cdh1. A prodrug of TAME arrests cells in metaphase without perturbing the spindle, but nonetheless the arrest is dependent on the SAC. Metaphase arrest induced by a proteasome inhibitor is also SAC dependent, suggesting that APC-dependent proteolysis is required to inactivate the SAC. We propose that mutual antagonism between the APC and the SAC yields a positive feedback loop that amplifies the ability of TAME to induce mitotic arrest.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cohesion fatigue explains why pharmacological inhibition of the APC/C induces a spindle checkpoint-dependent mitotic arrest.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049041. Epub 2012 Nov 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23145059 Free PMC article.
-
APC/C- and Mad2-mediated degradation of Cdc20 during spindle checkpoint activation.Cell Cycle. 2009 Jan 1;8(1):167-71. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.1.7606. Epub 2009 Jan 11. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19098431 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc20 proteolysis requires p38 MAPK signaling and Cdh1-independent APC/C ubiquitination during spindle assembly checkpoint activation by cadmium.J Cell Physiol. 2010 May;223(2):327-34. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22038. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20054826
-
Control of mitotic transitions by the anaphase-promoting complex.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Sep 29;354(1389):1583-90. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0502. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10582244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin A and Nek2A: APC/C-Cdc20 substrates invisible to the mitotic spindle checkpoint.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Feb;38(Pt 1):72-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0380072. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20074038 Review.
Cited by
-
_targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system for cancer therapy.Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2013 Sep;17(9):1091-108. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.815728. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2013. PMID: 23822887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damage associated with mitosis and cytokinesis failure.Oncogene. 2013 Sep 26;32(39):4593-601. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.615. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23318447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APC/C-mediated multiple monoubiquitylation provides an alternative degradation signal for cyclin B1.Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Jan 29;14(2):168-76. doi: 10.1038/ncb2425. Nat Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22286100 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms creating bistable switches at cell cycle transitions.Open Biol. 2013 Mar 13;3(3):120179. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120179. Open Biol. 2013. PMID: 23486222 Free PMC article.
-
PCBP1/HNRNP E1 Protects Chromosomal Integrity by Translational Regulation of CDC27.Mol Cancer Res. 2016 Jul;14(7):634-46. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0018. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Mol Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27102006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bekier ME, Fischbach R, Lee J, Taylor WR. Length of mitotic arrest induced by microtubule-stabilizing drugs determines cell death after mitotic exit. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:1646–1654. - PubMed
-
- Burton JL, Tsakraklides V, Solomon MJ. Assembly of an APC-Cdh1-substrate complex is stimulated by engagement of a destruction box. Mol Cell. 2005;18:533–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

