Steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) family: masters of systems biology
- PMID: 20956538
- PMCID: PMC2998129
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R110.193367
Steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) family: masters of systems biology
Abstract
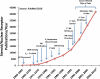
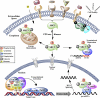
The three members of the p160 family of steroid receptor coactivators (SRC-1, SRC-2, and SRC-3) steer the functional output of numerous genetic programs and serve as pleiotropic rheostats for diverse physiological processes. Since their discovery ∼15 years ago, the extraordinary sum of examination of SRC function has shaped the foundation of our knowledge for the now 350+ coregulators that have been identified to date. In this perspective, we retrace our steps into the field of coregulators and provide a summary of selected seminal work that helped define the SRCs as masters of systems biology.
Figures
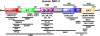
Similar articles
-
Steroid receptor coactivators: servants and masters for control of systems metabolism.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Jul;25(7):337-47. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24953190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An acetylation-enhanced interaction between transcription factor Sox2 and the steroid receptor coactivators facilitates Sox2 transcriptional activity and function.J Biol Chem. 2021 Dec;297(6):101389. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101389. Epub 2021 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34762910 Free PMC article.
-
miR-137 _targets p160 Steroid Receptor Coactivators SRC1, SRC2, and SRC3 and Inhibits Cell Proliferation.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Aug;29(8):1170-83. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1080. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26066330 Free PMC article.
-
Expression patterns of the steroid receptor coactivator family in human ovarian endometriosis.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2011 Oct;37(10):1269-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.2010.01509.x. Epub 2011 Apr 26. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2011. PMID: 21518137
-
Steroid receptor coactivators present a unique opportunity for drug development in hormone-dependent cancers.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 15;140:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28390937 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear receptor control of enterohepatic circulation.Compr Physiol. 2012 Oct;2(4):2811-28. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c120007. Compr Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23720266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-context dependent TCF/LEF expression and function: alternative tales of repression, de-repression and activation potentials.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2011;21(3):207-36. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v21.i3.10. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2011. PMID: 22111711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Expression Control by Glucocorticoid Receptors during Innate Immune Responses.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016 Apr 19;7:31. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00031. eCollection 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016. PMID: 27148162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steroid receptor coactivator-3 as a potential molecular _target for cancer therapy.Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2012 Nov;16(11):1085-96. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2012.718330. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2012. PMID: 22924430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of steroid receptor coactivators alleviates hyperglycemia-induced endothelial cell injury in rats through activating the PI3K/Akt pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 May;40(5):648-657. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0109-4. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30089865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. (1969) Science 165, 349–357 - PubMed
-
- Spelsberg T. C., Steggles A. W., O'Malley B. W. (1971) J. Biol. Chem. 246, 4188–4197 - PubMed
-
- Murray M. B., Towle H. C. (1989) Mol. Endocrinol. 3, 1434–1442 - PubMed
-
- Ma J., Ptashne M. (1988) Cell 55, 443–446 - PubMed
-
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. (1991) Cell 66, 563–576 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

