Identification of amino acid residues in protein SRP72 required for binding to a kinked 5e motif of the human signal recognition particle RNA
- PMID: 21073748
- PMCID: PMC2995471
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-83
Identification of amino acid residues in protein SRP72 required for binding to a kinked 5e motif of the human signal recognition particle RNA
Abstract
Background: Human cells depend critically on the signal recognition particle (SRP) for the sorting and delivery of their proteins. The SRP is a ribonucleoprotein complex which binds to signal sequences of secretory polypeptides as they emerge from the ribosome. Among the six proteins of the eukaryotic SRP, the largest protein, SRP72, is essential for protein _targeting and possesses a poorly characterized RNA binding domain.
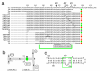
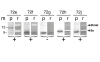
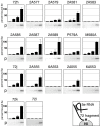
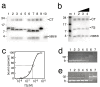
Results: We delineated the minimal region of SRP72 capable of forming a stable complex with an SRP RNA fragment. The region encompassed residues 545 to 585 of the full-length human SRP72 and contained a lysine-rich cluster (KKKKKKKKGK) at postions 552 to 561 as well as a conserved Pfam motif with the sequence PDPXRWLPXXER at positions 572 to 583. We demonstrated by site-directed mutagenesis that both regions participated in the formation of a complex with the RNA. In agreement with biochemical data and results from chymotryptic digestion experiments, molecular modeling of SRP72 implied that the invariant W577 was located inside the predicted structure of an RNA binding domain. The 11-nucleotide 5e motif contained within the SRP RNA fragment was shown by comparative electrophoresis on native polyacrylamide gels to conform to an RNA kink-turn. The model of the complex suggested that the conserved A240 of the K-turn, previously identified as being essential for the binding to SRP72, could protrude into a groove of the SRP72 RNA binding domain, similar but not identical to how other K-turn recognizing proteins interact with RNA.
Conclusions: The results from the presented experiments provided insights into the molecular details of a functionally important and structurally interesting RNA-protein interaction. A model for how a ligand binding pocket of SRP72 can accommodate a new RNA K-turn in the 5e region of the eukaryotic SRP RNA is proposed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of an RNA-binding domain in human SRP72.J Mol Biol. 2005 Jan 28;345(4):659-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.10.087. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15588816
-
Structures of human SRP72 complexes provide insights into SRP RNA remodeling and ribosome interaction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 9;45(1):470-481. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1124. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899666 Free PMC article.
-
The 5e motif of eukaryotic signal recognition particle RNA contains a conserved adenosine for the binding of SRP72.RNA. 2008 Jun;14(6):1143-53. doi: 10.1261/rna.979508. Epub 2008 Apr 25. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18441046 Free PMC article.
-
Archaea signal recognition particle shows the way.Archaea. 2010 Jun 28;2010:485051. doi: 10.1155/2010/485051. Archaea. 2010. PMID: 20672053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, function and evolution of the signal recognition particle.EMBO J. 2003 Jul 15;22(14):3479-85. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg337. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12853463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noncanoncial signal recognition particle RNAs in a major eukaryotic phylum revealed by purification of SRP from the human pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 15;43(18):9017-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv819. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26275773 Free PMC article.
-
Recognizing familial myeloid leukemia in adults.Ther Adv Hematol. 2013 Aug;4(4):254-69. doi: 10.1177/2040620713487399. Ther Adv Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23926458 Free PMC article.
-
Exome sequencing identifies autosomal-dominant SRP72 mutations associated with familial aplasia and myelodysplasia.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 May 4;90(5):888-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.020. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22541560 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical Functions and Cellular Dynamics of the Mammalian Signal Recognition Particle Components.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 25;8:679584. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.679584. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34113652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal recognition particle: an essential protein-_targeting machine.Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:693-721. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-072711-164732. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23414305 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Koch HG, Moser M, Muller M. Signal recognition particle-dependent protein _targeting, universal to all kingdoms of life. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;146:55–94. full_text. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

