Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 21173796
- PMCID: PMC3193406
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2010.177
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
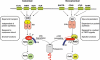
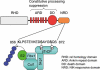
The non-canonical NF-κB pathway is an important arm of NF-κB signaling that predominantly _targets activation of the p52/RelB NF-κB complex. This pathway depends on the inducible processing of p100, a molecule functioning as both the precursor of p52 and a RelB-specific inhibitor. A central signaling component of the non-canonical pathway is NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK), which integrates signals from a subset of TNF receptor family members and activates a downstream kinase, IκB kinase-α (IKKα), for triggering p100 phosphorylation and processing. A unique mechanism of NIK regulation is through its fate control: the basal level of NIK is kept low by a TRAF-cIAP destruction complex and signal-induced non-canonical NF-κB signaling involves NIK stabilization. Tight control of the fate of NIK is important, since deregulated NIK accumulation is associated with lymphoid malignancies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Negative feedback in noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling modulates NIK stability through IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation.Sci Signal. 2010 May 25;3(123):ra41. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000778. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20501937 Free PMC article.
-
The noncanonical NF-κB pathway.Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):125-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01088.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22435551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon induces NF-kappa B-inducing kinase/tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-dependent NF-kappa B activation to promote cell survival.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 9;280(36):31530-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503120200. Epub 2005 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16009713 Free PMC article.
-
The NF-κB subunit RelB controls p100 processing by competing with the kinases NIK and IKK1 for binding to p100.Sci Signal. 2016 Sep 27;9(447):ra96. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aad9413. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 27678221
-
_targeting signaling factors for degradation, an emerging mechanism for TRAF functions.Immunol Rev. 2015 Jul;266(1):56-71. doi: 10.1111/imr.12311. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26085207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential response of IgM and IgG memory B cell populations to CD40L: insights of T cell - memory B cell interactions.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1432045. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1432045. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39050849 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and in silico analyses of MIF cytokine and TLR signalling interplay in the LPS inflammatory response of Ciona robusta.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 9;10(1):11339. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68339-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32647255 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile function of NF-ĸB in inflammation and cancer.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jul 16;13(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00529-z. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39014491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 redundancy differs between T and B cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 17;8(6):e66161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066161. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23799077 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PHLPP2/cyclin D1 protein translation contributes to the tumor suppressive effect of NFκB2 (p100).Onco_target. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):34112-30. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.8746. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 27095572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:693–733. - PubMed
-
- Dejardin E. The alternative NF-kappaB pathway from biochemistry to biology: pitfalls and promises for future drug development. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:1161–1179. - PubMed
-
- Xiao G, Harhaj EW, Sun SC. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. Mol Cell. 2001;7:401–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

