Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy
- PMID: 21205641
- PMCID: PMC3030664
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1196371
Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy
Abstract
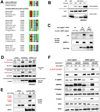
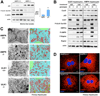
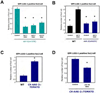
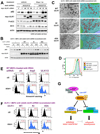
Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a conserved sensor of intracellular energy activated in response to low nutrient availability and environmental stress. In a screen for conserved substrates of AMPK, we identified ULK1 and ULK2, mammalian orthologs of the yeast protein kinase Atg1, which is required for autophagy. Genetic analysis of AMPK or ULK1 in mammalian liver and Caenorhabditis elegans revealed a requirement for these kinases in autophagy. In mammals, loss of AMPK or ULK1 resulted in aberrant accumulation of the autophagy adaptor p62 and defective mitophagy. Reconstitution of ULK1-deficient cells with a mutant ULK1 that cannot be phosphorylated by AMPK revealed that such phosphorylation is required for mitochondrial homeostasis and cell survival during starvation. These findings uncover a conserved biochemical mechanism coupling nutrient status with autophagy and cell survival.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cell biology. Why starving cells eat themselves.Science. 2011 Jan 28;331(6016):410-1. doi: 10.1126/science.1201691. Science. 2011. PMID: 21273476 No abstract available.
-
AMPK activates autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1.Circ Res. 2011 Apr 1;108(7):787-8. doi: 10.1161/RES.0b013e3182194c29. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21454792 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The association of AMPK with ULK1 regulates autophagy.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 3;5(11):e15394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015394. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21072212 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;13(2):132-41. doi: 10.1038/ncb2152. Epub 2011 Jan 23. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21258367 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of ULK1 regulates ATG9 localization.Autophagy. 2012 Aug;8(8):1197-214. doi: 10.4161/auto.20586. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Autophagy. 2012. PMID: 22932492 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase: An energy sensor and survival mechanism in the reinstatement of metabolic homeostasis.Exp Cell Res. 2023 Jul 1;428(1):113614. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113614. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Exp Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 37127064 Review.
-
Role of an intrinsically disordered conformation in AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of ULK1 and regulation of autophagy.Mol Biosyst. 2012 Jan;8(1):91-6. doi: 10.1039/c1mb05265a. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Mol Biosyst. 2012. PMID: 21853163 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between insulin sensitivity and gene expression in human skeletal muscle.BMC Endocr Disord. 2021 Feb 27;21(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00687-9. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021. PMID: 33639916 Free PMC article.
-
Signal Transduction and Molecular Regulation in Fatty Liver Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021 Sep 20;35(9):689-717. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0076. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021. PMID: 33906425 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of GSK3β increases basal autophagy and AMPK signalling in nutrient-laden human aortic endothelial cells.Biosci Rep. 2016 Sep 16;36(5):e00382. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160174. Print 2016 Oct. Biosci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27534430 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria and reactive oxygen species: physiology and pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Mar 19;14(3):6306-44. doi: 10.3390/ijms14036306. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23528859 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoregulation of the autophagy machinery by kinases and phosphatases.Autophagy. 2022 Jan;18(1):104-123. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1909407. Epub 2021 May 10. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 33970777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 CA009370-29/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006516-43/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080425-05/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01CA120964-01A/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080425/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30CA006516-43/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080425-04/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

