IL-6 promotes prostate tumorigenesis and progression through autocrine cross-activation of IGF-IR
- PMID: 21258401
- PMCID: PMC3112005
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.605
IL-6 promotes prostate tumorigenesis and progression through autocrine cross-activation of IGF-IR
Abstract
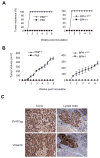
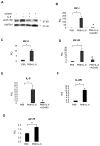
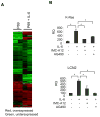
As an established mediator of inflammation, interleukin-6 (IL-6) is implicated to facilitate prostate cancer progression to androgen independence through transactivation of the androgen receptor. However, whether IL-6 has a causative role in de novo prostate tumorigenesis was never investigated. We now provide the first evidence that IL-6 can induce tumorigenic conversion and further progression to an invasive phenotype of non-tumorigenic benign prostate epithelial cells. Moreover, we find that paracrine IL-6 stimulates the autocrine IL-6 loop and autocrine activation of insulin-like type I growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) to confer the tumorigenic property and also that activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is critical in these processes. Inhibition of STAT3 activation or IGF-IR signaling suppresses IL-6-mediated malignant conversion and the associated invasive phenotype. Inhibition of STAT3 activation suppresses IL-6-induced upregulation of IGF-IR and its ligands, namely IGF-I and IGF-II. These findings indicate that IL-6 signaling cooperates with IGF-IR signaling in the prostate microenvironment to promote prostate tumorigenesis and progression to aggressiveness. Our findings suggest that STAT3 and IGF-IR may represent potential effective _targets for prevention or treatment of prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
_targeting heat shock protein 90 in pancreatic cancer impairs insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling, disrupts an interleukin-6/signal-transducer and activator of transcription 3/hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha autocrine loop, and reduces orthotopic tumor growth.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Nov 1;13(21):6459-68. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1104. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17975158
-
The ETS factor ESE3/EHF represses IL-6 preventing STAT3 activation and expansion of the prostate cancer stem-like compartment.Onco_target. 2016 Nov 22;7(47):76756-76768. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.12525. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 27732936 Free PMC article.
-
An androgen-IL-6-Stat3 autocrine loop re-routes EGF signal in prostate cancer cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007 May 30;270(1-2):50-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.02.006. Epub 2007 Feb 17. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17374439
-
Interaction of IGF signaling and the androgen receptor in prostate cancer progression.J Cell Biochem. 2006 Oct 1;99(2):392-401. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20929. J Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16639715 Review.
-
Implications of insulin-like growth factor-I for prostate cancer therapies.Int J Urol. 2009 Feb;16(2):161-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2008.02224.x. Epub 2008 Dec 5. Int J Urol. 2009. PMID: 19183230 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-6 and oncostatin-M synergize with the PI3K/AKT pathway to promote aggressive prostate malignancy in mouse and human tissues.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Oct;11(10):1159-65. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0238. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23867565 Free PMC article.
-
Early growth response 3 (Egr3) is highly over-expressed in non-relapsing prostate cancer but not in relapsing prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054096. Epub 2013 Jan 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23342084 Free PMC article.
-
Common salt aggravated pathology of testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in adult male Wistar rat.BMC Urol. 2023 Dec 11;23(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01371-x. BMC Urol. 2023. PMID: 38082261 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular plasticity and the neuroendocrine phenotype in prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2018 May;15(5):271-286. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2018.22. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Nat Rev Urol. 2018. PMID: 29460922 Review.
-
Senescent stroma promotes prostate cancer progression: the role of miR-210.Mol Oncol. 2014 Dec;8(8):1729-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2014.07.009. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Mol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25091736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Shanti N, Saini A, Faulkner SH, Stewart CE. Beneficial synergistic interactions of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in C2 skeletal myoblasts--potential cross-talk with IGF system. Growth Factors. 2008;26:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Bae VL, Jackson-Cook CK, Brothman AR, Maygarden SJ, Ware JL. Tumorigenicity of SV40 T antigen immortalized human prostate epithelial cells: association with decreased epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression. Int J Cancer. 1994;58:721–9. - PubMed
-
- Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A, et al. TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity. 2004;21:491–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

