Four faces of cellular senescence
- PMID: 21321098
- PMCID: PMC3044123
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201009094
Four faces of cellular senescence
Abstract
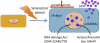
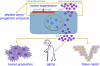
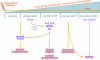
Cellular senescence is an important mechanism for preventing the proliferation of potential cancer cells. Recently, however, it has become apparent that this process entails more than a simple cessation of cell growth. In addition to suppressing tumorigenesis, cellular senescence might also promote tissue repair and fuel inflammation associated with aging and cancer progression. Thus, cellular senescence might participate in four complex biological processes (tumor suppression, tumor promotion, aging, and tissue repair), some of which have apparently opposing effects. The challenge now is to understand the senescence response well enough to harness its benefits while suppressing its drawbacks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
On the evolution of cellular senescence.Aging Cell. 2020 Dec;19(12):e13270. doi: 10.1111/acel.13270. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 33166065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular senescence: a link between cancer and age-related degenerative disease?Semin Cancer Biol. 2011 Dec;21(6):354-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.09.001. Epub 2011 Sep 10. Semin Cancer Biol. 2011. PMID: 21925603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular senescence: putting the paradoxes in perspective.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011 Feb;21(1):107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.10.005. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011. PMID: 21093253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescence under appraisal: hopes and challenges revisited.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Apr;78(7):3333-3354. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03746-x. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33439271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Premature aging/senescence in cancer cells facing therapy: good or bad?Biogerontology. 2016 Feb;17(1):71-87. doi: 10.1007/s10522-015-9593-9. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Biogerontology. 2016. PMID: 26330289 Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal analysis on inflammatory markers and frailty progression: based on the English longitudinal study of aging.Eur Geriatr Med. 2024 Oct;15(5):1323-1330. doi: 10.1007/s41999-024-00998-9. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Eur Geriatr Med. 2024. PMID: 38987423
-
Senescent cells: a novel therapeutic _target for aging and age-related diseases.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jan;93(1):105-16. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2012.193. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23212104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RelA: a tale of a stitch in time.J Clin Invest. 2016 Aug 1;126(8):2799-801. doi: 10.1172/JCI89156. Epub 2016 Jul 25. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27454293 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent turnover of senescent cells during regeneration of a complex structure.Elife. 2015 May 5;4:e05505. doi: 10.7554/eLife.05505. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25942455 Free PMC article.
-
FGFR4 Inhibitor BLU9931 Attenuates Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion While Inducing Senescence: Evidence for Senolytic Therapy Potential in Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 14;12(10):2976. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102976. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alimonti A., Nardella C., Chen Z., Clohessy J.G., Carracedo A., Trotman L.C., Cheng K., Varmeh S., Kozma S.C., Thomas G., et al. 2010. A novel type of cellular senescence that can be enhanced in mouse models and human tumor xenografts to suppress prostate tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 120:681–693 10.1172/JCI40535 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

