Airway fibroblasts in asthma manifest an invasive phenotype
- PMID: 21471104
- PMCID: PMC3136991
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201009-1452OC
Airway fibroblasts in asthma manifest an invasive phenotype
Abstract
Rationale: Invasive cell phenotypes have been demonstrated in malignant transformation, but not in other diseases, such as asthma. Cellular invasiveness is thought to be mediated by transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). IL-13 is a key T(H)2 cytokine that directs many features of airway remodeling through TGF-β1 and MMPs.
Objectives: We hypothesized that, in human asthma, IL-13 stimulates increased airway fibroblast invasiveness via TGF-β1 and MMPs in asthma compared with normal controls.
Methods: Fibroblasts were cultured from endobronchial biopsies in 20 subjects with mild asthma (FEV(1): 90 ± 3.6% pred) and 17 normal control subjects (FEV(1): 102 ± 2.9% pred) who underwent bronchoscopy. Airway fibroblast invasiveness was investigated using Matrigel chambers. IL-13 or IL-13 with TGF-β1 neutralizing antibody or pan-MMP inhibitor (GM6001) was added to the lower chamber as a chemoattractant. Flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry were performed in a subset of subjects to evaluate IL-13 receptor levels.
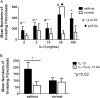
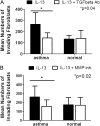
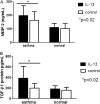
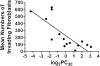
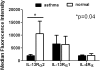
Measurements and main results: IL-13 significantly stimulated invasion in asthmatic airway fibroblasts, compared with normal control subjects. Inhibitors of both TGF-β1 and MMPs blocked IL-13-induced invasion in asthma, but had no effect in normal control subjects. At baseline, in airway tissue, IL-13 receptors were expressed in significantly higher levels in asthma, compared with normal control subjects. In airway fibroblasts, baseline IL-13Rα2 was reduced in asthma compared with normal control subjects.
Conclusions: IL-13 potentiates airway fibroblast invasion through a mechanism involving TGF-β1 and MMPs. IL-13 receptor subunits are differentially expressed in asthma. These effects may result in IL-13-directed airway remodeling in asthma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Action of 1,25(OH)2D3 on Human Asthmatic Bronchial Fibroblasts: Implications for Airway Remodeling in Asthma.J Asthma Allergy. 2020 Aug 12;13:249-264. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S261271. eCollection 2020. J Asthma Allergy. 2020. PMID: 32982316 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-13 induces collagen type-1 expression through matrix metalloproteinase-2 and transforming growth factor-β1 in airway fibroblasts in asthma.Eur Respir J. 2014 Feb;43(2):464-73. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00068712. Epub 2013 May 16. Eur Respir J. 2014. PMID: 23682108 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 augmentation by IL-13 on TGF-beta 1-stimulated primary human fibroblasts.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007 Jun;119(6):1388-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.02.011. Epub 2007 Apr 5. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17418380
-
Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases-1 and -2 in Interleukin-13-Suppressed Elastin in Airway Fibroblasts in Asthma.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Jan;54(1):41-50. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0290OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26074138 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta1 in asthmatic airway smooth muscle enlargement: is fibroblast growth factor-2 required?Clin Exp Allergy. 2010 May;40(5):710-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03497.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010. PMID: 20447083 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-4 and IL-13 signaling in allergic airway disease.Cytokine. 2015 Sep;75(1):68-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.014. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26070934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MIG-10 (Lamellipodin) stabilizes invading cell adhesion to basement membrane and is a negative transcriptional _target of EGL-43 in C. elegans.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Sep 26;452(3):328-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.049. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25148942 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Its Implications in Asthma.J Immunol Res. 2021 Feb 13;2021:6645072. doi: 10.1155/2021/6645072. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33628848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Action of 1,25(OH)2D3 on Human Asthmatic Bronchial Fibroblasts: Implications for Airway Remodeling in Asthma.J Asthma Allergy. 2020 Aug 12;13:249-264. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S261271. eCollection 2020. J Asthma Allergy. 2020. PMID: 32982316 Free PMC article.
-
IRAK-M Regulates Proliferative and Invasive Phenotypes of Lung Fibroblasts.Inflammation. 2023 Apr;46(2):763-778. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01772-4. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36577924
References
-
- Ingram JL, Antao-Menezes A, Mangum JB, Lyght O, Lee PJ, Elias JA, Bonner JC. Opposing actions of Stat1 and Stat6 on IL-13-induced up-regulation of early growth response-1 and platelet-derived growth factor ligands in pulmonary fibroblasts. J Immunol 2006;177:4141–4148. - PubMed
-
- Kraft M, Lewis C, Pham D, Chu HW. IL-4, IL-13, and dexamethasone augment fibroblast proliferation in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;107:602–606. - PubMed

