Tissue organization by cadherin adhesion molecules: dynamic molecular and cellular mechanisms of morphogenetic regulation
- PMID: 21527735
- PMCID: PMC3556819
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00004.2010
Tissue organization by cadherin adhesion molecules: dynamic molecular and cellular mechanisms of morphogenetic regulation
Abstract
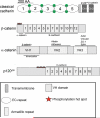
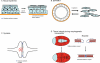
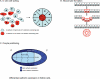
This review addresses the cellular and molecular mechanisms of cadherin-based tissue morphogenesis. Tissue physiology is profoundly influenced by the distinctive organizations of cells in organs and tissues. In metazoa, adhesion receptors of the classical cadherin family play important roles in establishing and maintaining such tissue organization. Indeed, it is apparent that cadherins participate in a range of morphogenetic events that range from support of tissue integrity to dynamic cellular rearrangements. A comprehensive understanding of cadherin-based morphogenesis must then define the molecular and cellular mechanisms that support these distinct cadherin biologies. Here we focus on four key mechanistic elements: the molecular basis for adhesion through cadherin ectodomains, the regulation of cadherin expression at the cell surface, cooperation between cadherins and the actin cytoskeleton, and regulation by cell signaling. We discuss current progress and outline issues for further research in these fields.
Figures
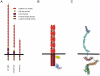

Similar articles
-
Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator.Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1451-5. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419. Science. 1991. PMID: 2006419 Review.
-
Cadherins in development: cell adhesion, sorting, and tissue morphogenesis.Genes Dev. 2006 Dec 1;20(23):3199-214. doi: 10.1101/gad.1486806. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 17158740 Review.
-
Classical cadherin adhesion molecules: coordinating cell adhesion, signaling and the cytoskeleton.J Mol Histol. 2004 Nov;35(8-9):839-44. doi: 10.1007/s10735-004-1833-2. J Mol Histol. 2004. PMID: 15609097 Review.
-
Cell adhesion: the molecular basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis.Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):345-57. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81279-9. Cell. 1996. PMID: 8608588 Review.
-
Cadherin-catenin complex: protein interactions and their implications for cadherin function.J Cell Biochem. 1996 Jun 15;61(4):514-23. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19960616)61:4%3C514::AID-JCB4%3E3.0.CO;2-R. J Cell Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8806074 Review.
Cited by
-
Prostaglandins in cancer cell adhesion, migration, and invasion.Int J Cell Biol. 2012;2012:723419. doi: 10.1155/2012/723419. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Int J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22505934 Free PMC article.
-
Keratins control intercellular adhesion involving PKC-α-mediated desmoplakin phosphorylation.J Cell Biol. 2013 May 27;201(5):681-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201208162. Epub 2013 May 20. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23690176 Free PMC article.
-
Cadherin-based intercellular adhesions organize epithelial cell-matrix traction forces.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 15;110(3):842-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217279110. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23277553 Free PMC article.
-
P120 catenin potentiates constitutive E-cadherin dimerization at the plasma membrane and regulates trans binding.Curr Biol. 2021 Jul 26;31(14):3017-3027.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.04.061. Epub 2021 May 20. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34019823 Free PMC article.
-
Classical and desmosomal cadherins at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2012 Jun 1;125(Pt 11):2547-52. doi: 10.1242/jcs.066654. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22833291 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abe K, Chisaka O, van Roy F, Takeichi M. Stability of dendritic spines and synaptic contacts is controlled by aN-catenin. Nat Neurosci. 2004 - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Stehbens SJ, Yap AS. Touch, grasp, deliver and control: functional cross-talk between microtubules and cell adhesions. Traffic. 2009;10:268–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

