Expression of leptin, leptin receptor, adiponectin, and adiponectin receptor in ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive breast cancer
- PMID: 21847403
- PMCID: PMC3148540
- DOI: 10.4048/jbc.2011.14.2.96
Expression of leptin, leptin receptor, adiponectin, and adiponectin receptor in ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Adipocytokines, such as leptin, resistin, and adiponectin, are associated with obesity and breast cancer. Several studies have indicated that adipocytokines may influence tumor growth or differentiation. The aims of this study were to determine the expression of leptin, leptin receptor (ObR), adiponectin and adiponectin receptor (AdipoR) in human breast cancer, to evaluate their prognostic significance in the breast cancer.
Methods: Specimens from 198 patients with primary breast cancer were enrolled, and representative paraffin tumor blocks were selected for constructing tissue microarrarys (TMA). Immunohistochemical staining for leptin, ObR, adiponectin, and AdipoR was performed using TMA, and the clinicopathologic characteristics were evaluated from the patient's medical records.
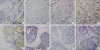
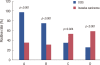
Results: Stage 0 breast cancer accounted for 41 cases, and 157 cases were invasive cancer. Positive rates of leptin and ObR expression in the ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) group were significantly higher than those of the invasive cancer group (97.4% vs. 34.0%, p<0.001; 74.4% vs. 29.8%, p<0.001). However, positive rates of adiponectin and AdipoR expression in the invasive cancer group were significantly higher than those in the DCIS group (53.7% vs. 33.3%, p=0.024; 59.9% vs. 26.3%, p<0.001). High leptin expression was significantly associated with high Ki-67 expression (p=0.016). High adiponectin expression was significantly correlated with smaller tumor size (p=0.001).
Conclusion: We suggest that losses of leptin and ObR expression could be associated with invasive cancer, whereas high adiponectin and AdipoR expression may be associated with breast cancer invasiveness.
Keywords: Adipocytokine; Adiponectin; Breast neoplasms; Leptin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of adiponectin, leptin, and their receptors in ovarian endometrioma.Fertil Steril. 2013 Jul;100(1):135-41.e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.03.019. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Fertil Steril. 2013. PMID: 23579009
-
Clinicopathological roles of adiponectin and leptin receptors in endometrial carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2014 Apr;7(4):1109-1117. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.1846. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24944677 Free PMC article.
-
Imbalance in leptin-adiponectin levels and leptin receptor expression as chief contributors to triple negative breast cancer progression in Northeast India.Gene. 2017 Jul 20;621:51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.04.021. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28414093
-
Changes in insulin resistance following bariatric surgery and the adipoinsular axis: role of the adipocytokines, leptin, adiponectin and resistin.Obes Surg. 2005 May;15(5):692-9. doi: 10.1381/0960892053923789. Obes Surg. 2005. PMID: 15946462 Review.
-
Adipocytokines and breast cancer.Curr Probl Cancer. 2018 Mar-Apr;42(2):208-214. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Curr Probl Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29433827 Review.
Cited by
-
Triple-negative breast cancer: new perspectives for novel therapies.Med Oncol. 2013;30(3):653. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0653-1. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Med Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23824643 Review.
-
Adiponectin as Link Factor between Adipose Tissue and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 15;20(4):839. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040839. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30781341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Adipokine Component in the Molecular Regulation of Cancer Cell Survival, Proliferation and Metastasis.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Sep 13;27:1609828. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.1609828. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34588926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association analysis of genetic variants of adiponectin gene and risk of pancreatic cancer.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 May 15;8(5):8094-100. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26221375 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Pathways Induced by Leptin during Epithelial⁻Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 6;19(11):3493. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113493. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reinier KS, Vacek PM, Geller BM. Risk factors for breast carcinoma in situ versus invasive breast cancer in a prospective study of pre- and post-menopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;103:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Stephenson GD, Rose DP. Breast cancer and obesity: an update. Nutr Cancer. 2003;45:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam A, Dorgan JF, Longcope C, et al. Body mass index, serum sex hormones, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:1218–1226. - PubMed
-
- Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O'Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 2004;363:1346–1353. - PubMed
-
- Vona-Davis L, Rose DP. Angiogenesis, adipokines and breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20:193–201. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

