Unidirectional cross-activation of GRPR by MOR1D uncouples itch and analgesia induced by opioids
- PMID: 22000021
- PMCID: PMC3197217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.043
Unidirectional cross-activation of GRPR by MOR1D uncouples itch and analgesia induced by opioids
Abstract
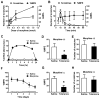
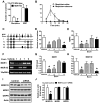
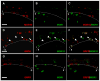
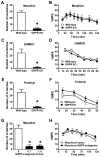
Spinal opioid-induced itch, a prevalent side effect of pain management, has been proposed to result from pain inhibition. We now report that the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) isoform MOR1D is essential for morphine-induced scratching (MIS), whereas the isoform MOR1 is required only for morphine-induced analgesia (MIA). MOR1D heterodimerizes with gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR) in the spinal cord, relaying itch information. We show that morphine triggers internalization of both GRPR and MOR1D, whereas GRP specifically triggers GRPR internalization and morphine-independent scratching. Providing potential insight into opioid-induced itch prevention, we demonstrate that molecular and pharmacologic inhibition of PLCβ3 and IP3R3, downstream effectors of GRPR, specifically block MIS but not MIA. In addition, blocking MOR1D-GRPR association attenuates MIS but not MIA. Together, these data suggest that opioid-induced itch is an active process concomitant with but independent of opioid analgesia, occurring via the unidirectional cross-activation of GRPR signaling by MOR1D heterodimerization.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
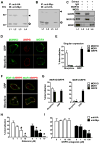
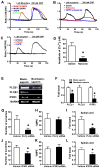
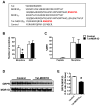
Comment in
-
Why does morphine make you itch?Cell. 2011 Oct 14;147(2):261-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.026. Cell. 2011. PMID: 22000005
Similar articles
-
Central opioid receptors mediate morphine-induced itch and chronic itch via disinhibition.Brain. 2021 Mar 3;144(2):665-681. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa430. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33367648
-
Physiological function of gastrin-releasing peptide and neuromedin B receptors in regulating itch scratching behavior in the spinal cord of mice.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 24;8(6):e67422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067422. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826298 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between Human Spinal Cord μ-opioid Receptor 1Y Isoform and Gastrin-releasing Peptide Receptor Mediates Opioid-induced Scratching Behavior.Anesthesiology. 2019 Aug;131(2):381-391. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002776. Anesthesiology. 2019. PMID: 31314749 Free PMC article.
-
Neural processing of itch.Neuroscience. 2013 Oct 10;250:697-714. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.07.035. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23891755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism of μ-opioid receptor (MOR)-TRPV1 crosstalk in TRPV1 activation involves morphine anti-nociception, tolerance and dependence.Channels (Austin). 2015;9(5):235-43. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1069450. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Channels (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26176938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral mechanisms of itch.Neurosci Bull. 2012 Apr;28(2):100-10. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1202-1. Neurosci Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NPY2R signaling gates spontaneous and mechanical, but not thermal, pain transmission.Mol Pain. 2019 Jan-Dec;15:1744806919887830. doi: 10.1177/1744806919887830. Mol Pain. 2019. PMID: 31646939 Free PMC article.
-
TRP Channels as Drug _targets to Relieve Itch.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018 Oct 6;11(4):100. doi: 10.3390/ph11040100. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30301231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing acidosis: nociception or sngception?J Biomed Sci. 2018 Nov 29;25(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0486-5. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 30486810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
μ-Opioid receptors in primary sensory neurons are essential for opioid analgesic effect on acute and inflammatory pain and opioid-induced hyperalgesia.J Physiol. 2019 Mar;597(6):1661-1675. doi: 10.1113/JP277428. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30578671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbadie C, Pan Y, Drake CT, Pasternak GW. Comparative immunohistochemical distributions of carboxy terminus epitopes from the mu-opioid receptor splice variants MOR-1D, MOR-1 and MOR-1C in the mouse and rat CNS. Neuroscience. 2000;100:141–153. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Ferre S, Lluis C, Franco R, Fuxe K. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutical implications of intramembrane receptor/receptor interactions among heptahelical receptors with examples from the striatopallidal GABA neurons. Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55:509–550. - PubMed
-
- Andoh T, Yageta Y, Konno M, Yamaguchi-Miyamoto T, Takahata H, Nojima H, Nemoto H, Kuraishi Y. Evidence for separate involvement of different mu-opioid receptor subtypes in itch and analgesia induced by supraspinal action of opioids. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008;106:667–670. - PubMed
-
- Ballantyne JC, Loach AB, Carr DB. Itching after epidural and spinal opiates. Pain. 1988;33:149–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

