A new chapter in the transcription SAGA
- PMID: 22014650
- PMCID: PMC3232345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2011.09.004
A new chapter in the transcription SAGA
Abstract
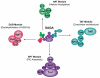
Eukaryotic transcriptional coactivators are multi-subunit complexes that both modify chromatin and recognize histone modifications. Until recently, structural information on these large complexes has been limited to isolated enzymatic domains or chromatin-binding motifs. This review summarizes recent structural studies of the SAGA coactivator complex that have greatly advanced our understanding of the interplay between its different subunits. The structure of the four-protein SAGA deubiquitinating module has provided a first glimpse of the larger organization of a coactivator complex, and illustrates how interdependent subunits interact with each other to form an active and functional enzyme complex. In addition, structures of the histone binding domains of ATXN7 and Sgf29 shed light on the interactions with chromatin that help recruit the SAGA complex.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

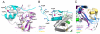
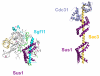
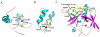
Similar articles
-
SAGA and TFIID: Friends of TBP drifting apart.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194604. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32673655 Review.
-
Mapping the deubiquitination module within the SAGA complex.Structure. 2014 Nov 4;22(11):1553-9. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.07.017. Structure. 2014. PMID: 25441028
-
The SAGA chromatin-modifying complex: the sum of its parts is greater than the whole.Genes Dev. 2020 Oct 1;34(19-20):1287-1303. doi: 10.1101/gad.341156.120. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 33004486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The promiscuity of the SAGA complex subunits: Multifunctional or moonlighting proteins?Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194607. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194607. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32712338 Review.
-
Conformational flexibility and subunit arrangement of the modular yeast Spt-Ada-Gcn5 acetyltransferase complex.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 17;290(16):10057-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.624684. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25713136 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Global SUMO Proteome Responses Guide Gene Regulation, mRNA Biogenesis, and Plant Stress Responses.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Sep 17;3:215. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00215. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 23060889 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast two-hybrid screening reveals a dual function for the histone acetyltransferase GcnE by controlling glutamine synthesis and development in Aspergillus fumigatus.Curr Genet. 2019 Apr;65(2):523-538. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0891-z. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30324432
-
Histone H2B ubiquitination promotes the function of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 Jun 19;4(8):1529-38. doi: 10.1534/g3.114.012625. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 24948786 Free PMC article.
-
Dissenting degradation: Deubiquitinases in cell cycle and cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Dec;67(Pt 2):145-158. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.03.008. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 32201366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of DUBs Regulation in Signaling and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 20;22(3):986. doi: 10.3390/ijms22030986. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33498168 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee TI, Young RA. Transcription of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Annu Rev Genet. 2000;34:77–137. - PubMed
-
- Weake VM, Workman JL. Inducible gene expression: diverse regulatory mechanisms. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:426–437. - PubMed
-
- Naar AM, Lemon BD, Tjian R. Transcriptional coactivator complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:475–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

