Serial measurements of NT-proBNP are predictive of not-high-dose anthracycline cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 22068815
- PMCID: PMC3242597
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.439
Serial measurements of NT-proBNP are predictive of not-high-dose anthracycline cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess the value of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in predicting late cardiotoxicity in patients treated with not-high-dose chemotherapy (NHDC), and to compare the predictive value of NT-proBNP and cardiac troponin I (cTnI).
Methods: In 71 patients undergoing NHDC with anthracyclines, NT-proBNP and cTnI levels were measured before and 24 h after each NHDC cycle. Left ventricular (LV) function was assessed by echocardiography at baseline, every two NHDC cycles, at the end of chemotherapy, and at 3-, 6- and 12-month follow-up.
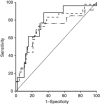
Results: During NHDC, only NT-proBNP showed abnormal values. According to NT-proBNP behaviour, patients were divided into two groups: group A (n=50) with normal (n=23) or transiently elevated NT-proBNP levels (n=27), and group B (n=21) with persistently elevated NT-proBNP levels. At follow-up, LV impairment was significantly worse in group B than in group A. %Δ (baseline-peak) NT-proBNP was predictive of LV impairment at 3-, 6- and 12-month follow-up, with a cutoff of 36%.
Conclusion: Serial measurements of NT-proBNP may be a useful tool for the early detection of patients treated with NHDC at high risk of developing cardiotoxicity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Use of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide to assess left ventricular function after adjuvant doxorubicin therapy in early breast cancer patients: a prospective series.Clin Drug Investig. 2009;29(2):131-7. doi: 10.2165/0044011-200929020-00007. Clin Drug Investig. 2009. PMID: 19133708
-
Assessment of echocardiography and biomarkers for the extended prediction of cardiotoxicity in patients treated with anthracyclines, taxanes, and trastuzumab.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012 Sep 1;5(5):596-603. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.973321. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22744937 Free PMC article.
-
New biomarkers for early detection of cardiotoxicity after treatment with docetaxel, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide.Biomarkers. 2015 Mar;20(2):143-8. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2015.1040839. Epub 2015 May 18. Biomarkers. 2015. PMID: 25980453
-
Serum NT-proBNP in the early detection of doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jun;9(2):155-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-7563.2012.01588.x. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22897825
-
Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 29;13(21):5426. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215426. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can we find a good biochemical marker of early cardiotoxicity in children treated with haematopoietic stem cell transplantation?Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2016;20(3):220-4. doi: 10.5114/wo.2016.61563. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2016. PMID: 27647986 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Cardiovascular Biomarkers in Cancer Therapeutics-Related Cardiotoxicity: Review of Critical Challenges, Solutions, and Future Directions.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Nov 7;12(21):e029574. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.029574. Epub 2023 Oct 27. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37889193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in Cardiovascular Biomarkers With Breast Cancer Therapy and Associations With Cardiac Dysfunction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jan 21;9(2):e014708. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014708. Epub 2020 Jan 21. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 31959034 Free PMC article.
-
2-Deoxy-d-Glucose (2-DG)-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Rat: NT-proBNP and BNP as Potential Early Cardiac Safety Biomarkers.Int J Toxicol. 2016 May;35(3):284-93. doi: 10.1177/1091581815624397. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Int J Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26838190 Free PMC article.
-
Coronary artery disease, left ventricular function and cardiac biomarkers determine all-cause mortality in cancer patients-a large monocenter cohort study.Clin Res Cardiol. 2023 Feb;112(2):203-214. doi: 10.1007/s00392-022-02001-6. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Clin Res Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 35312818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamcova M, Sterba M, Simunek T, Potacova A, Popelova O, Mazurova Y, Gersl V (2005) Troponin as a marker of myocardiac damage in drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Expert Opin Drug Saf 4: 457–472 - PubMed
-
- Auner HW, Tinchon C, Linkesch W, Tiran A, Quehenberger F, Link H, Sill H (2003) Prolonged monitoring of troponin T for the detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity in adults with hematological malignancies. Ann Hematol 82: 218–222 - PubMed
-
- Bauch M, Ester A, Kimura B, Victorica BE, Kedar A, Phillips MI (1992) Atrial natriuretic peptide as a marker for doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxic effects. Cancer 69: 1492–1497 - PubMed
-
- Cardinale D, Colombo A, Lamantia G, Colombo N, Civelli M, De Giacomi G, Rubino M, Veglia F, Fiorentini C, Cipolla CM (2010) Anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy: clinical relevance and response to pharmacologic therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 55: 213–220 - PubMed
-
- Cardinale D, Sandri MT, Colombo A, Colombo N, Boeri M, Lamantia G, Civelli M, Peccatori F, Martinelli G, Fiorentini C, Cipolla CM (2004) Prognostic value of troponin I in cardiac risk stratification of cancer patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy. Circulation 109: 2749–2754 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

