CHEK2 contribution to hereditary breast cancer in non-BRCA families
- PMID: 22114986
- PMCID: PMC3326561
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3062
CHEK2 contribution to hereditary breast cancer in non-BRCA families
Abstract
Background: Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are responsible for only a part of hereditary breast cancer (HBC). The origins of "non-BRCA" HBC in families may be attributed in part to rare mutations in genes conferring moderate risk, such as CHEK2, which encodes for an upstream regulator of BRCA1. Previous studies have demonstrated an association between CHEK2 founder mutations and non-BRCA HBC. However, very few data on the entire coding sequence of this gene are available.
Methods: We investigated the contribution of CHEK2 mutations to non-BRCA HBC by direct sequencing of its whole coding sequence in 507 non-BRCA HBC cases and 513 controls.
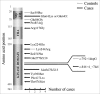
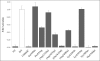
Results: We observed 16 mutations in cases and 4 in controls, including 9 missense variants of uncertain consequence. Using both in silico tools and an in vitro kinase activity test, the majority of the variants were found likely to be deleterious for protein function. One variant present in both cases and controls was proposed to be neutral. Removing this variant from the pool of potentially deleterious variants gave a mutation frequency of 1.48% for cases and 0.29% for controls (P = 0.0040). The odds ratio of breast cancer in the presence of a deleterious CHEK2 mutation was 5.18.
Conclusions: Our work indicates that a variety of deleterious CHEK2 alleles make an appreciable contribution to breast cancer susceptibility, and their identification could help in the clinical management of patients carrying a CHEK2 mutation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Frequency of the CHEK2 1100delC mutation among women with early-onset and bilateral breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 20;14(2):401. doi: 10.1186/bcr3159. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22520019 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Screening for BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, PALB2, BRIP1, RAD50, and CDH1 mutations in high-risk Finnish BRCA1/2-founder mutation-negative breast and/or ovarian cancer individuals.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 28;13(1):R20. doi: 10.1186/bcr2832. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21356067 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in PALB2, CHEK2, and other known breast cancer susceptibility genes among 1054 BRCA-negative Hispanics with breast cancer.Cancer. 2019 Aug 15;125(16):2829-2836. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32083. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31206626 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, and TP53 in families at high risk of breast cancer.JAMA. 2006 Mar 22;295(12):1379-88. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.12.1379. JAMA. 2006. PMID: 16551709
-
[The clinical importance of a genetic analysis of moderate-risk cancer susceptibility genes in breast and other cancer patients from the Czech Republic].Klin Onkol. 2012;25 Suppl:S59-66. Klin Onkol. 2012. PMID: 22920209 Review. Czech.
-
Spectrum and frequency of CHEK2 variants in breast cancer affected and general population in the Baltic states region, initial results and literature review.Eur J Med Genet. 2022 May;65(5):104477. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2022.104477. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Eur J Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 35314380 Review.
Cited by
-
Feedback of extended panel sequencing in 1530 patients referred for suspicion of hereditary predisposition to adult cancers.Clin Genet. 2021 Jan;99(1):166-175. doi: 10.1111/cge.13864. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Clin Genet. 2021. PMID: 33047316 Free PMC article.
-
Germline Predisposition to Pediatric Cancer, from Next Generation Sequencing to Medical Care.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 24;13(21):5339. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215339. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771502 Free PMC article.
-
DNA repair genes implicated in triple negative familial non-BRCA1/2 breast cancer predisposition.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 15;5(7):2113-26. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26328243 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of High-to-Moderate Penetrance Genes on Genetic Testing: Looking over Breast Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 26;14(8):1530. doi: 10.3390/genes14081530. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628581 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the use of molecular dynamics in assessing protein variants for phenotypic alterations.Hum Mutat. 2019 Sep;40(9):1424-1435. doi: 10.1002/humu.23800. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Hum Mutat. 2019. PMID: 31106920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahman N, Seal S, Thompson D, Kelly P, Renwick A, Elliott A, Reid S, Spanova K, Barfoot R, Chagtai T, Jayatilake H, McGuffog L, Hanks S, Evans DG, Eccles D. Breast Cancer Susceptibility Collaboration (UK) Easton DF, Stratton MR. PALB2, which encodes a BRCA2-interacting protein, is a breast cancer susceptibility gene. Nat Genet. 2007;39:165–167. doi: 10.1038/ng1959. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meijers-Heijboer H, van den Ouweland A, Klijn J, Wasielewski M, de Snoo A, Oldenburg R, Hollestelle A, Houben M, Crepin E, van Veghel-Plandsoen M, Elstrodt F, van Duijn C, Bartels C, Meijers C, Schutte M, McGuffog L, Thompson D, Easton D, Sodha N, Seal S, Barfoot R, Mangion J, Chang-Claude J, Eccles D, Eeles R, Evans DG, Houlston R, Murday V, Narod S, Peretz T, Peto J, Phelan C, Zhang HX, Szabo C, Devilee P, Goldgar D, Futreal PA, Nathanson KL, Weber B, Rahman N, Stratton MR. CHEK2-Breast Cancer Consortium. Low-penetrance susceptibility to breast cancer due to CHEK2*1100delC in noncarriers of BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. Nat Genet. 2002;31:55–59. doi: 10.1038/ng879. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Renwick A, Thompson D, Seal S, Kelly P, Chagtai T, Ahmed M, North B, Jayatilake H, Barfoot R, Spanova K, McGuffog L, Evans DG, Eccles D. Breast Cancer Susceptibility Collaboration (UK) Easton DF, Stratton MR, Rahman N. ATM mutations that cause ataxia-telangiectasia are breast cancer susceptibility alleles. Nat Genet. 2006;38:873–875. doi: 10.1038/ng1837. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seal S, Thompson D, Renwick A, Elliott A, Kelly P, Barfoot R, Chagtai T, Jayatilake H, Ahmed M, Spanova K, North B, McGuffog L, Evans DG, Eccles D. Breast Cancer Susceptibility Collaboration (UK) Easton DF, Stratton MR, Rahman N. Truncating mutations in the Fanconi anemia J gene BRIP1 are low-penetrance breast cancer susceptibility alleles. Nat Genet. 2006;38:1239–1241. doi: 10.1038/ng1902. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

