Autophagy in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 22291707
- PMCID: PMC3265076
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/760498
Autophagy in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
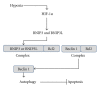
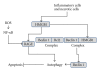
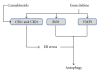
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a devastating disease with an extremely poor life expectancy and no effective treatment. Autophagy is a process of degradation of cytoplasmic component capable of recycling cellular components or eliminate specific _targets. The presence of autophagy in PDAC has been demonstrated. However, the implicated cellular pathways are not fully understood and, more importantly, the role of autophagy in PDAC is matter of intensive debate. This review summarizes recently published data in an attempt to clarify the importance of autophagy in this disease and try to reconcile apparently contradictory results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autophagy as a therapeutic _target in pancreatic cancer.Br J Cancer. 2021 Jan;124(2):333-344. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01039-5. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32929194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UBL4A inhibits autophagy-mediated proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via _targeting LAMP1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 9;38(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1278-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31288830 Free PMC article.
-
_targets (Metabolic Mediators) of Therapeutic Importance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 12;21(22):8502. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228502. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33198082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGFB1-induced autophagy affects the pattern of pancreatic cancer progression in distinct ways depending on SMAD4 status.Autophagy. 2020 Mar;16(3):486-500. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1628540. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31177911 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Survival Pathways MAPK and NF-kB Triggers Apoptosis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells via Suppression of Autophagy._target Oncol. 2016 Apr;11(2):183-95. doi: 10.1007/s11523-015-0388-3. _target Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26373299
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Aspects and Molecular _targets of Autophagy to Control Pancreatic Cancer Management.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 20;10(6):1459. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061459. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel histone deacetylase inhibitor AR-42 exhibits antitumor activity in pancreatic cancer cells by affecting multiple biochemical pathways.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 22;12(8):e0183368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183368. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28829799 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy: a double-edged sword for neuronal survival after cerebral ischemia.Neural Regen Res. 2014 Jun 15;9(12):1210-6. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.135329. Neural Regen Res. 2014. PMID: 25206784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conceptual framework for cutting the pancreatic cancer fuel supply.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 15;18(16):4285-90. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0041. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22896695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy-Mediated Exosomes as Immunomodulators of Natural Killer Cells in Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 19;10:622956. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.622956. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33680945 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

