Mutations in the DDR2 kinase gene identify a novel therapeutic _target in squamous cell lung cancer
- PMID: 22328973
- PMCID: PMC3274752
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8274.CD-11-0005
Mutations in the DDR2 kinase gene identify a novel therapeutic _target in squamous cell lung cancer
Abstract
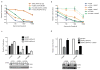
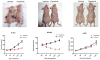
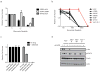
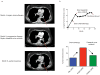
While genomically _targeted therapies have improved outcomes for patients with lung adenocarcinoma, little is known about the genomic alterations which drive squamous cell lung cancer. Sanger sequencing of the tyrosine kinome identified mutations in the DDR2 kinase gene in 3.8% of squamous cell lung cancers and cell lines. Squamous lung cancer cell lines harboring DDR2 mutations were selectively killed by knock-down of DDR2 by RNAi or by treatment with the multi-_targeted kinase inhibitor dasatinib. Tumors established from a DDR2 mutant cell line were sensitive to dasatinib in xenograft models. Expression of mutated DDR2 led to cellular transformation which was blocked by dasatinib. A squamous cell lung cancer patient with a response to dasatinib and erlotinib treatment harbored a DDR2 kinase domain mutation. These data suggest that gain-of-function mutations in DDR2 are important oncogenic events and are amenable to therapy with dasatinib. As dasatinib is already approved for use, these findings could be rapidly translated into clinical trials.
Significance: DDR2 mutations are present in 4% of lung SCCs, and DDR2 mutations are associated with sensitivity to dasatinib. These findings provide a rationale for designing clinical trials with the FDA-approved drug dasatinib in patients with lung SCCs.
Keywords: DDR2; Squamous cell lung cancer; dasatinib; lung cancer genomics; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: M.M. is a consultant to Novartis and receives research support from Novartis, receives research support from Genentech, is a founding advisor and consultant to, and an equity holder in, Foundation Medicine and patent holder for EGFR mutation testing, licensed to Genzyme Genetics. N.S.G. receives research support from Novartis. E B.H. was the principal investigator of an industry-sponsored clinical trial of dasatinib and erlotinib in lung cancer funded in part by Bristol-Myers-Squibb and the American Society for Clinical Oncology. R.K.T. reports consulting and lecture fees (Sequenom, Sanofi-Aventis, Merck, Roche, Infinity, Boehringer, Astra-Zeneca, Johnson&Johnson, Atlas-Biolabs) and research support (Novartis, AstraZeneca).
Figures

Comment in
-
A new _target for therapy in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.Cancer Discov. 2011 Jun;1(1):23-4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8274.CD-11-0069. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Cancer Discov. 2011. PMID: 22586316
Similar articles
-
Adaptive responses to dasatinib-treated lung squamous cell cancer cells harboring DDR2 mutations.Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;74(24):7217-7228. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0505. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25348954 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired resistance to dasatinib in lung cancer cell lines conferred by DDR2 gatekeeper mutation and NF1 loss.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Feb;13(2):475-82. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0817. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24296828 Free PMC article.
-
NSCLC Driven by DDR2 Mutation Is Sensitive to Dasatinib and JQ1 Combination Therapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Oct;14(10):2382-2389. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0077. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26206333 Free PMC article.
-
Discoidin domain receptor 2 signaling networks and therapy in lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2014 Jun;9(6):900-4. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000164. J Thorac Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24828669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancers: an update for recent advances in therapeutics.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016 Jun;22(3):461-76. doi: 10.1177/1078155215577810. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016. PMID: 25855240 Review.
Cited by
-
Next-Generation Sequencing at High Sequencing Depth as a Tool to Study the Evolution of Metastasis Driven by Genetic Change Events of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 5;10:1215. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01215. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32903616 Free PMC article.
-
Refining the treatment of NSCLC according to histological and molecular subtypes.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015 Sep;12(9):511-26. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.90. Epub 2015 May 12. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25963091 Review.
-
Phenotype-genotype correlation in multiple primary lung cancer patients in China.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 31;6:36177. doi: 10.1038/srep36177. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27796337 Free PMC article.
-
DDR2 polymorphisms and mRNA expression in lung cancers of Japanese patients.Oncol Lett. 2012 Jul;4(1):33-37. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.684. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22807955 Free PMC article.
-
Type I collagen aging impairs discoidin domain receptor 2-mediated tumor cell growth suppression.Onco_target. 2016 May 3;7(18):24908-27. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.8795. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 27121132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lennes IT, Lynch TJ. Quality indicators in cancer care: development and implementation for improved health outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;10(5):341–6. - PubMed
-
- West H, Harpole D, Travis W. Histologic considerations for individualized systemic therapy approaches for the management of non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 2009;136(4):1112–8. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304(5676):1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21):2129–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

