Phase I study of anti-CD22 immunoconjugate inotuzumab ozogamicin plus rituximab in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 22335424
- PMCID: PMC7659250
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02241.x
Phase I study of anti-CD22 immunoconjugate inotuzumab ozogamicin plus rituximab in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
Inotuzumab ozogamicin (CMC-544), a humanized anti-CD22 antibody conjugated to the potent cytotoxic antibiotic calicheamicin, _targets the CD22 antigen expressed on the majority of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. This phase I study assessed the tolerability, safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy of inotuzumab ozogamicin administered intravenously in combination with rituximab in Japanese patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Ten patients were administered rituximab 375 mg/m(2) followed by inotuzumab ozogamicin at the maximum tolerated dose (1.8 mg/m(2)). Treatment was repeated every 28 days up to eight cycles, or until occurrence of disease progression or intolerable toxicity. The safety profile was similar to that of inotuzumab ozogamicin monotherapy, with hematologic adverse events occurring most frequently. The most common grade three or higher adverse events were thrombocytopenia (70%), neutropenia (50%), leukopenia (30%), and lymphopenia (30%). The overall response rate was 80% (8/10; 95% CI, 44-98%). Drug exposure increased with successive doses, similar to the pharmacokinetic profiles observed in previous phase I monotherapy studies. Efficacy results suggested promising antitumor activity, and the overall findings support the continued clinical development of this therapeutic regimen in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. This trial was registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov as NCT00724971.
© 2012 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and clinical activity of a combination therapy comprising two antibody-based _targeting agents for the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: results of a phase I/II study evaluating the immunoconjugate inotuzumab ozogamicin with rituximab.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Feb 10;31(5):573-83. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.7211. Epub 2013 Jan 7. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23295790 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I Study of Inotuzumab Ozogamicin Combined with R-CVP for Relapsed/Refractory CD22+ B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 1;22(19):4807-4816. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2488. Epub 2016 May 6. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27154915 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I study of inotuzumab ozogamicin (CMC-544) in Japanese patients with follicular lymphoma pretreated with rituximab-based therapy.Cancer Sci. 2010 Aug;101(8):1840-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01601.x. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20491780 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inotuzumab Ozogamicin: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2017 Sep;77(14):1603-1610. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0802-5. Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28819740 Review.
-
Preclinical and clinical development of inotuzumab-ozogamicin in hematological malignancies.Mol Immunol. 2015 Oct;67(2 Pt A):107-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25304309 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel CD20 monoclonal antibodies for lymphoma therapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2012 Oct 11;5:64. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-5-64. J Hematol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23057966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Integration of Antibody-Drug Conjugate in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.Curr Oncol Rep. 2015 Sep;17(9):41. doi: 10.1007/s11912-015-0466-9. Curr Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26194424 Review.
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates: Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modeling, Preclinical Characterization, Clinical Studies, and Lessons Learned.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Jun;57(6):687-703. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0619-0. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29188435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical parameters for design and development of multivalent nanoconstructs: recent trends.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Oct;12(10):2335-2358. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-01103-4. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35013982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Randomized, phase 3 trial of inotuzumab ozogamicin plus rituximab versus chemotherapy plus rituximab for relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Br J Haematol. 2018 Aug;182(4):583-586. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14820. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Br J Haematol. 2018. PMID: 28677896 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
References
-
- Leonard JP, Coleman M, Ketas JC et al Epratuzumab, a humanized anti‐CD22 antibody, in aggressive non‐Hodgkin's lymphoma: phase I/II clinical trial results. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 5327–34. - PubMed
-
- DiJoseph JF, Armellino DC, Boghaert ER et al Antibody‐_targeted chemotherapy with CMC‐544: a CD22‐_targeted immunoconjugate of calicheamicin for the treatment of B‐lymphoid malignancies. Blood 2004; 103: 1807–14. - PubMed
-
- DiJoseph JF, Khandke K, Dougher MM et al CMC‐544 (inotuzumab ozogamicin): a CD22‐_targeted immunoconjugate of calicheamicin. Hematol Meet Rep 2008; 5: 74–7.
-
- DiJoseph JF, Goad ME, Dougher MM et al Potent and specific antitumor efficacy of CMC‐544, a CD22‐_targeted immunoconjugate of calicheamicin, against systemically disseminated B‐cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 8620–9. - PubMed
-
- DiJoseph JF, Dougher MM, Kalyandrug LB et al Antitumor efficacy of a combination of CMC‐544 (inotuzumab ozogamicin), a CD22‐_targeted cytotoxic immunoconjugate of calicheamicin, and rituximab against non‐Hodgkin's B‐cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 242–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

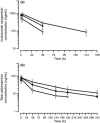
 ); cycle 2 (
); cycle 2 ( ); cycle 3 (
); cycle 3 ( ).
).