Large-scale cellular-resolution gene profiling in human neocortex reveals species-specific molecular signatures
- PMID: 22500809
- PMCID: PMC3328777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.052
Large-scale cellular-resolution gene profiling in human neocortex reveals species-specific molecular signatures
Abstract
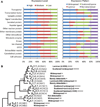
Although there have been major advances in elucidating the functional biology of the human brain, relatively little is known of its cellular and molecular organization. Here we report a large-scale characterization of the expression of ∼1,000 genes important for neural functions by in situ hybridization at a cellular resolution in visual and temporal cortices of adult human brains. These data reveal diverse gene expression patterns and remarkable conservation of each individual gene's expression among individuals (95%), cortical areas (84%), and between human and mouse (79%). A small but substantial number of genes (21%) exhibited species-differential expression. Distinct molecular signatures, comprised of genes both common between species and unique to each, were identified for each major cortical cell type. The data suggest that gene expression profile changes may contribute to differential cortical function across species, and in particular, a shift from corticosubcortical to more predominant corticocortical communications in the human brain.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Shared and distinct transcriptomic cell types across neocortical areas.Nature. 2018 Nov;563(7729):72-78. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0654-5. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30382198 Free PMC article.
-
An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome.Nature. 2012 Sep 20;489(7416):391-399. doi: 10.1038/nature11405. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22996553 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of layer-specific genes in Mammalian neocortex.Cereb Cortex. 2007 Aug;17(8):1918-33. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhl102. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Cereb Cortex. 2007. PMID: 17065549
-
Gene expression profiling of primate neocortex: molecular neuroanatomy of cortical areas.Genes Brain Behav. 2006;5 Suppl 1:38-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2006.00193.x. Genes Brain Behav. 2006. PMID: 16417616 Review.
-
Comparative molecular neuroanatomy of mammalian neocortex: what can gene expression tell us about areas and layers?Dev Growth Differ. 2009 Apr;51(3):343-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2008.01085.x. Epub 2009 Feb 16. Dev Growth Differ. 2009. PMID: 19222526 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered gene expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia.Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Apr;19(4):478-85. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.30. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Mol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23528911 Free PMC article.
-
High spatial resolution proteomic comparison of the brain in humans and chimpanzees.J Comp Neurol. 2015 Oct 1;523(14):2043-61. doi: 10.1002/cne.23777. Epub 2015 Jul 14. J Comp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25779868 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Economic Behavior Patterns Are Constructed from Finite, Genetically Controlled Modules of Behavior.Cell Rep. 2019 Aug 13;28(7):1814-1829.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.038. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31412249 Free PMC article.
-
LaminaRGeneVis: A Tool to Visualize Gene Expression Across the Laminar Architecture of the Human Neocortex.Front Neuroinform. 2022 Feb 24;16:753770. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2022.753770. eCollection 2022. Front Neuroinform. 2022. PMID: 35281717 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse engineering human brain evolution using organoid models.Brain Res. 2020 Feb 15;1729:146582. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146582. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31809699 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

