Altered subcellular localization of transcription factor TEAD4 regulates first mammalian cell lineage commitment
- PMID: 22529382
- PMCID: PMC3358889
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1201595109
Altered subcellular localization of transcription factor TEAD4 regulates first mammalian cell lineage commitment
Abstract
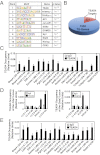
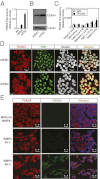
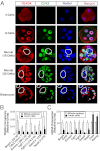
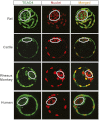
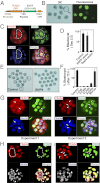
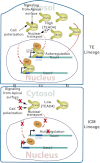
In the preimplantation mouse embryo, TEAD4 is critical to establishing the trophectoderm (TE)-specific transcriptional program and segregating TE from the inner cell mass (ICM). However, TEAD4 is expressed in the TE and the ICM. Thus, differential function of TEAD4 rather than expression itself regulates specification of the first two cell lineages. We used ChIP sequencing to define genomewide TEAD4 _target genes and asked how transcription of TEAD4 _target genes is specifically maintained in the TE. Our analyses revealed an evolutionarily conserved mechanism, in which lack of nuclear localization of TEAD4 impairs the TE-specific transcriptional program in inner blastomeres, thereby allowing their maturation toward the ICM lineage. Restoration of TEAD4 nuclear localization maintains the TE-specific transcriptional program in the inner blastomeres and prevents segregation of the TE and ICM lineages and blastocyst formation. We propose that altered subcellular localization of TEAD4 in blastomeres dictates first mammalian cell fate specification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Tead4 is constitutively nuclear, while nuclear vs. cytoplasmic Yap distribution is regulated in preimplantation mouse embryos.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 11;109(50):E3389-90; author reply E3391-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211810109. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23169672 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
TEAD4 regulates trophectoderm differentiation upstream of CDX2 in a GATA3-independent manner in the human preimplantation embryo.Hum Reprod. 2022 Jul 30;37(8):1760-1773. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deac138. Hum Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35700449
-
Changes in the expression patterns of the genes involved in the segregation and function of inner cell mass and trophectoderm lineages during porcine preimplantation development.J Reprod Dev. 2013;59(2):151-8. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2012-122. Epub 2012 Dec 20. J Reprod Dev. 2013. PMID: 23257836 Free PMC article.
-
Tead4 is required for specification of trophectoderm in pre-implantation mouse embryos.Mech Dev. 2008 Mar-Apr;125(3-4):270-83. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Nov 17. Mech Dev. 2008. PMID: 18083014
-
Mechanisms of trophectoderm fate specification in preimplantation mouse development.Dev Growth Differ. 2010 Apr;52(3):263-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2009.01158.x. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Dev Growth Differ. 2010. PMID: 20100249 Review.
-
Establishment of trophectoderm and inner cell mass lineages in the mouse embryo.Mol Reprod Dev. 2009 Nov;76(11):1019-32. doi: 10.1002/mrd.21057. Mol Reprod Dev. 2009. PMID: 19479991 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factor AP-2γ induces early Cdx2 expression and represses HIPPO signaling to specify the trophectoderm lineage.Development. 2015 May 1;142(9):1606-15. doi: 10.1242/dev.120238. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Development. 2015. PMID: 25858457 Free PMC article.
-
A tale of two cell-fates: role of the Hippo signaling pathway and transcription factors in early lineage formation in mouse preimplantation embryos.Mol Hum Reprod. 2020 Sep 1;26(9):653-664. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaaa052. Mol Hum Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32647873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TEAD4 as an Oncogene and a Mitochondrial Modulator.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 5;10:890419. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.890419. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35602596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional annotation of colon cancer risk SNPs.Nat Commun. 2014 Sep 30;5:5114. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6114. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25268989 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomy of a blastocyst: cell behaviors driving cell fate choice and morphogenesis in the early mouse embryo.Genesis. 2013 Apr;51(4):219-33. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22368. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Genesis. 2013. PMID: 23349011 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zernicka-Goetz M. Cleavage pattern and emerging asymmetry of the mouse embryo. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:919–928. - PubMed
-
- Yagi R, et al. Transcription factor TEAD4 specifies the trophectoderm lineage at the beginning of mammalian development. Development. 2007;134:3827–3836. - PubMed
-
- Ralston A, et al. Gata3 regulates trophoblast development downstream of Tead4 and in parallel to Cdx2. Development. 2010;137:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Nishioka N, et al. Tead4 is required for specification of trophectoderm in pre-implantation mouse embryos. Mech Dev. 2008;125:270–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- HL094892/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD045611/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 RR021876/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL106311/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD062546/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL094892/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL106311/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD53925/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR000167/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR21876/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011106/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HD062546/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000167/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD053925/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

