SIRT1 protects against emphysema via FOXO3-mediated reduction of premature senescence in mice
- PMID: 22546858
- PMCID: PMC3366403
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI60132
SIRT1 protects against emphysema via FOXO3-mediated reduction of premature senescence in mice
Abstract
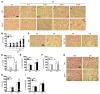
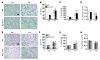
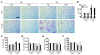
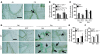
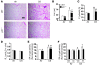
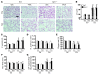
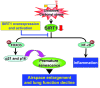
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/emphysema (COPD/emphysema) is characterized by chronic inflammation and premature lung aging. Anti-aging sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), a NAD+-dependent protein/histone deacetylase, is reduced in lungs of patients with COPD. However, the molecular signals underlying the premature aging in lungs, and whether SIRT1 protects against cellular senescence and various pathophysiological alterations in emphysema, remain unknown. Here, we showed increased cellular senescence in lungs of COPD patients. SIRT1 activation by both genetic overexpression and a selective pharmacological activator, SRT1720, attenuated stress-induced premature cellular senescence and protected against emphysema induced by cigarette smoke and elastase in mice. Ablation of Sirt1 in airway epithelium, but not in myeloid cells, aggravated airspace enlargement, impaired lung function, and reduced exercise tolerance. These effects were due to the ability of SIRT1 to deacetylate the FOXO3 transcription factor, since Foxo3 deficiency diminished the protective effect of SRT1720 on cellular senescence and emphysematous changes. Inhibition of lung inflammation by an NF-κB/IKK2 inhibitor did not have any beneficial effect on emphysema. Thus, SIRT1 protects against emphysema through FOXO3-mediated reduction of cellular senescence, independently of inflammation. Activation of SIRT1 may be an attractive therapeutic strategy in COPD/emphysema.
Figures
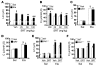
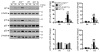
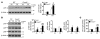
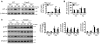
Similar articles
-
FOXO3 Activation Prevents Cellular Senescence in Emphysema Induced by Cigarette Smoke.COPD. 2023 Dec;20(1):80-91. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2022.2164262. Epub 2023 Jan 19. COPD. 2023. PMID: 36656684
-
Sirtuin 1 Activator SRT1720 Protects Against Lung Injury via Reduction of Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cells Apoptosis in Emphysema.COPD. 2015 Aug;12(4):444-52. doi: 10.3109/15412555.2014.974740. COPD. 2015. PMID: 25415045
-
SIRT1/FoxO3 axis alteration leads to aberrant immune responses in bronchial epithelial cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Apr;22(4):2272-2282. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13509. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29411515 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 as a therapeutic _target in inflammaging of the pulmonary disease.Prev Med. 2012 May;54 Suppl(Suppl):S20-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2011.11.014. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Prev Med. 2012. PMID: 22178470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox regulation of SIRT1 in inflammation and cellular senescence.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Aug;61:95-110. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.03.015. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23542362 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of histone deacetylase 2 in epigenetics and cellular senescence: implications in lung inflammaging and COPD.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Oct 1;303(7):L557-66. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00175.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22842217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hyperoxic-Hypoxic Paradox.Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 25;10(6):958. doi: 10.3390/biom10060958. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32630465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Death in the Lung: The Apoptosis-Necroptosis Axis.Annu Rev Physiol. 2019 Feb 10;81:375-402. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020518-114320. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Annu Rev Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30485762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 as a Potential Therapeutic _target for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Lung. 2023 Apr;201(2):201-215. doi: 10.1007/s00408-023-00607-9. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Lung. 2023. PMID: 36790647 Review.
-
Nobiletin ameliorates hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury through the activation of SIRT-1/FOXO3a-mediated autophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis.Exp Mol Med. 2019 Apr 26;51(4):1-16. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0245-z. Exp Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31028246 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

