TFIID TAF6-TAF9 complex formation involves the HEAT repeat-containing C-terminal domain of TAF6 and is modulated by TAF5 protein
- PMID: 22696218
- PMCID: PMC3431708
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.379206
TFIID TAF6-TAF9 complex formation involves the HEAT repeat-containing C-terminal domain of TAF6 and is modulated by TAF5 protein
Abstract
The general transcription factor TFIID recognizes specifically the core promoter of genes transcribed by eukaryotic RNA polymerase II, nucleating the assembly of the preinitiation complex at the transcription start site. However, the understanding in molecular terms of TFIID assembly and function remains poorly understood. Histone fold motifs have been shown to be extremely important for the heterodimerization of many TFIID subunits. However, these subunits display several evolutionary conserved noncanonical features when compared with histones, including additional regions whose role is unknown. Here we show that the conserved additional C-terminal region of TFIID subunit TAF6 can be divided into two domains: a small middle domain (TAF6M) and a large C-terminal domain (TAF6C). Our crystal structure of the TAF6C domain from Antonospora locustae at 1.9 Å resolution reveals the presence of five conserved HEAT repeats. Based on these data, we designed several mutants that were introduced into full-length human TAF6. Surprisingly, the mutants affect the interaction between TAF6 and TAF9, suggesting that the formation of the complex between these two TFIID subunits do not only depend on their histone fold motifs. In addition, the same mutants affect even more strongly the interaction between TAF6 and TAF9 in the context of a TAF5-TAF6-TAF9 complex. Expression of these mutants in HeLa cells reveals that most of them are unstable, suggesting their poor incorporation within endogenous TFIID. Taken together, our results suggest that the conserved additional domains in histone fold-containing subunits of TFIID and of co-activator SAGA are important for the assembly of these complexes.
Figures


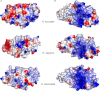
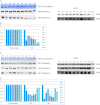

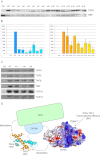
Similar articles
-
Mutational analysis of TAF6 revealed the essential requirement of the histone-fold domain and the HEAT repeat domain for transcriptional activation.FEBS J. 2018 Apr;285(8):1491-1510. doi: 10.1111/febs.14423. Epub 2018 Mar 23. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29485702
-
The TAF9 C-terminal conserved region domain is required for SAGA and TFIID promoter occupancy to promote transcriptional activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 May;34(9):1547-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01060-13. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24550006 Free PMC article.
-
TAF4 nucleates a core subcomplex of TFIID and mediates activated transcription from a TATA-less promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12347-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605499103. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16895980 Free PMC article.
-
SAGA and TFIID: Friends of TBP drifting apart.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194604. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32673655 Review.
-
Recent advances in understanding the structure and function of general transcription factor TFIID.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Jul;66(13):2123-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0009-3. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19308322 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics and transcription regulation during eukaryotic diversification: the saga of TFIID.Genes Dev. 2019 Aug 1;33(15-16):888-902. doi: 10.1101/gad.300475.117. Epub 2019 May 23. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 31123066 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into the structure of TFIID, its assembly, and its binding to core promoter.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2020 Apr;61:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2019.10.001. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 31751889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards a mechanistic understanding of core promoter recognition from cryo-EM studies of human TFIID.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2017 Dec;47:60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2017.05.015. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28624568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine mapping of QTL conferring Cercospora leaf spot disease resistance in mungbean revealed TAF5 as candidate gene for the resistance.Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Feb;134(2):701-714. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03724-8. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Theor Appl Genet. 2021. PMID: 33188437
-
The architecture of human general transcription factor TFIID core complex.Nature. 2013 Jan 31;493(7434):699-702. doi: 10.1038/nature11791. Epub 2013 Jan 6. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23292512
References
-
- Roeder R. G. (1996) The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 327–335 - PubMed
-
- Thomas M. C., Chiang C. M. (2006) The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41, 105–178 - PubMed
-
- Burley S. K., Roeder R. G. (1996) Biochemistry and structural biology of transcription factor IID (TFIID). Annu. Rev. Biochem. 65, 769–799 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

