Molecular mechanisms responsible for the selective and low-grade induction of proinflammatory mediators in murine macrophages by lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 22706082
- PMCID: PMC3392521
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200857
Molecular mechanisms responsible for the selective and low-grade induction of proinflammatory mediators in murine macrophages by lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
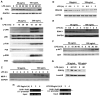
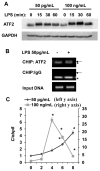
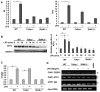
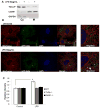
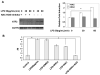
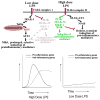
Low-dose endotoxemia is prevalent in humans with adverse health conditions, and it correlates with the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis, diabetes, and neurologic inflammation. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, we demonstrate that subclinical low-dose LPS skews macrophages into a mild proinflammatory state, through cell surface TLR4, IL-1R-associated kinase-1, and the Toll-interacting protein. Unlike high-dose LPS, low-dose LPS does not induce robust activation of NF-κB, MAPKs, PI3K, or anti-inflammatory mediators. Instead, low-dose LPS induces activating transcription factor 2 through Toll-interacting protein-mediated generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, allowing mild induction of proinflammatory mediators. Low-dose LPS also suppresses PI3K and related negative regulators of inflammatory genes. Our data reveal novel mechanisms responsible for skewed and persistent low-grade inflammation, a cardinal feature of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low-dose endotoxin induces inflammation by selectively removing nuclear receptors and activating CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein δ.J Immunol. 2011 Apr 1;186(7):4467-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003300. Epub 2011 Feb 25. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21357541
-
Immune complex/Ig negatively regulate TLR4-triggered inflammatory response in macrophages through Fc gamma RIIb-dependent PGE2 production.J Immunol. 2009 Jan 1;182(1):554-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.554. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19109188
-
Molecular mechanism responsible for the priming of macrophage activation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 8;288(6):3897-906. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.424390. Epub 2012 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23264622 Free PMC article.
-
IRAK4 kinase activity is not required for induction of endotoxin tolerance but contributes to TLR2-mediated tolerance.J Leukoc Biol. 2013 Aug;94(2):291-300. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0812401. Epub 2013 May 21. J Leukoc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23695305 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of in vitro reprogramming by Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 agonists in murine macrophages: effects of TLR "homotolerance" versus "heterotolerance" on NF-kappa B signaling pathway components.J Immunol. 2003 Jan 1;170(1):508-19. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.508. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12496438
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms responsible for the reduced expression of cholesterol transporters from macrophages by low-dose endotoxin.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Jan;33(1):24-33. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300049. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23117655 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of OASIS/CREB3L1 in podocytes contributes to the disturbance of kidney homeostasis.Commun Biol. 2022 Jul 22;5(1):734. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03709-x. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35869269 Free PMC article.
-
The cellular basis of organ failure in sepsis-signaling during damage and repair processes.Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2020 May;115(Suppl 1):4-9. doi: 10.1007/s00063-020-00673-4. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2020. PMID: 32236799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deacetylation by SIRT1 Reprograms Inflammation and Cancer.Genes Cancer. 2013 Mar;4(3-4):135-47. doi: 10.1177/1947601913476948. Genes Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24020005 Free PMC article.
-
Programming and memory dynamics of innate leukocytes during tissue homeostasis and inflammation.J Leukoc Biol. 2017 Sep;102(3):719-726. doi: 10.1189/jlb.6MR0117-027RR. Epub 2017 May 5. J Leukoc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28476750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes. 2008;57:1470–1481. - PubMed
-
- Wiedermann CJ, Kiechl S, Dunzendorfer S, Schratzberger P, Egger G, Oberhollenzer F, Willeit J. Association of endotoxemia with carotid atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease prospective results from the Bruneck Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999;34:1975–1981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

