The Nla28S/Nla28 two-component signal transduction system regulates sporulation in Myxococcus xanthus
- PMID: 22753068
- PMCID: PMC3415486
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00225-12
The Nla28S/Nla28 two-component signal transduction system regulates sporulation in Myxococcus xanthus
Abstract
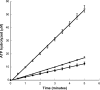
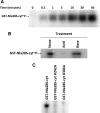
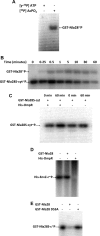
The response regulator Nla28 is a key component in a cascade of transcriptional activators that modulates expression of many important developmental genes in Myxococcus xanthus. In this study, we identified and characterized Nla28S, a histidine kinase that modulates the activity of this important regulator of M. xanthus developmental genes. We show that the putative cytoplasmic domain of Nla28S has the in vitro biochemical properties of a histidine kinase protein: it hydrolyzes ATP and undergoes an ATP-dependent autophosphorylation that is acid labile and base stable. We also show that the putative cytoplasmic domain of Nla28S transfers a phosphoryl group to Nla28 in vitro, that the phosphotransfer is specific, and that a substitution in the predicted site of Nla28 phosphorylation (aspartate 53) abolishes the phosphotransfer reaction. In phenotypic studies, we found that a mutation in nla28S produces a developmental phenotype similar to, but weaker than, that produced by a mutation in nla28; both mutations primarily affect sporulation. Together, these data indicate that Nla28S is the in vivo histidine kinase partner of Nla28 and that the primary function of the Nla28S/Nla28 two-component signal transduction system is to regulate sporulation genes. The results of genetic studies suggest that phosphorylation of Nla28S is important for the in vivo sporulation function of the Nla28S/Nla28 two-component system. In addition, the quorum signal known as A-signal is important for full developmental expression of the nla28S-nla28 operon, suggesting that quorum signaling regulates the availability of the Nla28S/Nla28 signal transduction circuit in developing cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems That Regulate the Temporal and Spatial Expression of Myxococcus xanthus Sporulation Genes.J Bacteriol. 2015 Sep 14;198(3):377-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.00474-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26369581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TodK, a putative histidine protein kinase, regulates timing of fruiting body morphogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2003 Sep;185(18):5452-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.18.5452-5464.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12949097 Free PMC article.
-
CrdS and CrdA comprise a two-component system that is cooperatively regulated by the Che3 chemosensory system in Myxococcus xanthus.mBio. 2011 Aug 2;2(4):e00110-11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00110-11. Print 2011. mBio. 2011. PMID: 21810965 Free PMC article.
-
EspA, an orphan hybrid histidine protein kinase, regulates the timing of expression of key developmental proteins of Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jul;190(13):4416-26. doi: 10.1128/JB.00265-08. Epub 2008 Apr 4. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18390653 Free PMC article.
-
Dual regulation with Ser/Thr kinase cascade and a His/Asp TCS in Myxococcus xanthus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:111-21. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792684 Review.
Cited by
-
The Evolution of Aggregative Multicellularity and Cell-Cell Communication in the Dictyostelia.J Mol Biol. 2015 Nov 20;427(23):3722-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 15. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26284972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The enhancer binding protein Nla6 regulates developmental genes that are important for Myxococcus xanthus sporulation.J Bacteriol. 2015 Apr;197(7):1276-87. doi: 10.1128/JB.02408-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25645554 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous Reversions of an Evolutionary Trait Loss Reveal Regulators of a Small RNA That Controls Multicellular Development in Myxobacteria.J Bacteriol. 2016 Nov 4;198(23):3142-3151. doi: 10.1128/JB.00389-16. Print 2016 Dec 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27621281 Free PMC article.
-
GcsR, a TyrR-Like Enhancer-Binding Protein, Regulates Expression of the Glycine Cleavage System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.mSphere. 2016 Apr 27;1(2):e00020-16. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00020-16. eCollection 2016 Mar-Apr. mSphere. 2016. PMID: 27303730 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressor mutations reveal an NtrC-like response regulator, NmpR, for modulation of Type-IV Pili-dependent motility in Myxococcus xanthus.PLoS Genet. 2018 Oct 22;14(10):e1007714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007714. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30346960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dutta R, Inouye M. 2000. GHKL, an emergent ATPase/kinase superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25:24–28 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

