Ubiquitin proteasome system in Parkinson's disease: a keeper or a witness?
- PMID: 22921536
- PMCID: PMC4077023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.08.008
Ubiquitin proteasome system in Parkinson's disease: a keeper or a witness?
Abstract
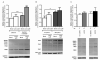
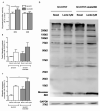
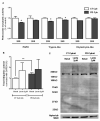
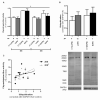
Objective: The aim of this work was to evaluate the role of ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) on mitochondrial-driven alpha-synuclein (aSN) clearance in in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo Parkinson's disease (PD) cellular models.
Method: We used SH-SY5Y ndufa2 knock-down (KD) cells, PD cybrids and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from patients meeting the diagnostic criteria for PD. We quantified aSN aggregation, proteasome activity and protein ubiquitination levels. In PBMC of PD patient population we evaluated the aSN levels in the plasma and the influence of several demographic characteristics in the above mentioned determinations.
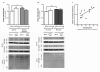
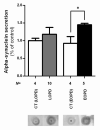
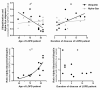
Results: We found that ubiquitin-independent proteasome activity was up-regulated in SH-SY5Y ndufa2 KD cells while a downregulation was observed in PD cybrids and PBMC. Moreover, we observed an increase in protein ubiquitination that correlates with a decrease in ubiquitin-dependent proteasome activity. Accordingly, proteasome inhibition prevented ubiquitin-dependent aSN clearance. Ubiquitin-independent proteasome activity was positively correlated with ubiquitination in PBMC. We also report a negative correlation of chymotrypsin-like activity with age in control and late-onset PD groups. Total ubiquitin content is positively correlated with aSN oligomer levels, which leads to an age-dependent increase of aSN ubiquitination in LOPD. Moreover, aSN levels are increased in the plasma of PD patients.
Interpretation: aSN oligomers are ubiquitinated and we identified a ubiquitin-dependent clearance insufficiency with the accumulation of both aSN and ubiquitin. However, SH-SY5Y ndufa2 KD cells showed a significant up-regulation of ubiquitin-independent proteasomal enzymatic activity that could mean a cell rescue attempt. Moreover, we identified that UPS function is age-dependent in PBMC.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
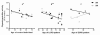
Comment in
-
Alpha-synuclein and protein degradation pathways in Parkinson's disease: a pathological feed-back loop.Exp Neurol. 2013 Sep;247:308-13. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.03.005. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Exp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23499831 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Protein Ubiquitination by Paraquat and 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium Impairs Ubiquitin-Dependent Protein Degradation Pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;53(8):5229-51. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9414-9. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26409479 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Study of a Parkinson's Disease Model of Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells Induced by a Proteasome Inhibitor.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jan 1;16(1):84-92. doi: 10.7150/ijms.28595. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30662332 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ubiquitin linkages on alpha-synuclein induced-toxicity in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2009 Jul;110(1):208-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06124.x. Epub 2009 Apr 27. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19457126
-
Ubiquitin-proteasome system and Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 2006 Nov;21(11):1806-23. doi: 10.1002/mds.21013. Mov Disord. 2006. PMID: 16972273 Review.
-
Ubiquitin-proteasome system and Parkinson's diseases.Exp Neurol. 2005 Feb;191 Suppl 1:S17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.08.021. Exp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15629758 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Analysis of FBXO2, FBXO6, FBXO12, and FBXO41 Variants in Han Chinese Patients with Sporadic Parkinson's Disease.Neurosci Bull. 2017 Oct;33(5):510-514. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0122-5. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Neurosci Bull. 2017. PMID: 28341977 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's Disease: Biomarkers, Treatment, and Risk Factors.Front Neurosci. 2018 Aug 30;12:612. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00612. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30214392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of Parkinsonian Pathology and Neurodegeneration in Mice After Long-Term Injections of a Proteasome Inhibitor in Olfactory Bulb and Amygdala.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Oct 21;13:698979. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.698979. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34744683 Free PMC article.
-
The interrelationship of proteasome impairment and oligomeric intermediates in neurodegeneration.Aging Cell. 2015 Oct;14(5):715-24. doi: 10.1111/acel.12359. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Aging Cell. 2015. PMID: 26053162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Protein Ubiquitination by Paraquat and 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium Impairs Ubiquitin-Dependent Protein Degradation Pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;53(8):5229-51. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9414-9. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26409479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arduino DM, Esteves AR, Oliveira CR, Cardoso SM. Mitochondrial metabolism modulation: a new therapeutic approach for Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug _targets. 2010;9:105–119. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MC, Bishop JF, Leng Y, Chock PB, Chase TN, Mouradian MM. Degradation of alpha-synuclein by proteasome. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:33855–33858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

