Cross-sectional and longitudinal association of body mass index and brain volume
- PMID: 23008165
- PMCID: PMC3615109
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.22159
Cross-sectional and longitudinal association of body mass index and brain volume
Abstract
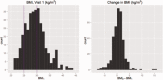
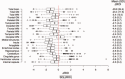
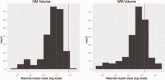
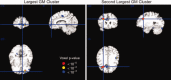
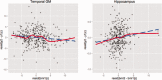
Although a link between body mass index (BMI) and brain volume has been established in several cross-sectional studies, evidence of the association between change in BMI over time and changes in brain structure is limited. Using data from a cohort of 347 former lead workers and community controls with two magnetic resonance imaging scans over a period of ~5 years, we estimated cross-sectional and longitudinal associations of BMI and brain volume using both region of interest (ROI) and voxel-based morphometric (VBM) methods. We found that associations of BMI and brain volume were not significantly different in former lead workers when compared with community controls. In the cross-sectional analysis, higher BMIs were associated with smaller brain volumes in gray matter (GM) using both ROI and VBM approaches. No associations with white matter (WM) were observed. In the longitudinal analysis, higher baseline BMI was associated with greater decline in temporal and occipital GM ROI volumes. Change in BMI over the 5-year period was only associated with change in hippocampal volume and was not associated with change in any of the GM ROIs. Overall, higher BMI was associated with lower GM volume in several ROIs and with declines in volume in temporal and occipital GM over time. These results suggest that sustained high body mass may contribute to progressive temporal and occipital atrophy.
Keywords: BMI; MRI; aging; brain structure; obesity.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal loss of gray matter volume in patients with first-episode schizophrenia: DARTEL automated analysis and ROI validation.Neuroimage. 2012 Jan 16;59(2):986-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.066. Epub 2011 Sep 5. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 21924364 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Children and Young Adults With CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2018 Sep;72(3):349-359. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.11.024. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 29398180 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of regional gray and white matter volumes to current BMI and future increases in BMI: a prospective MRI study.Int J Obes (Lond). 2012 May;36(5):656-64. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2011.175. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012. PMID: 21894161 Free PMC article.
-
Following the Spreading of Brain Structural Changes in Alzheimer's Disease: A Longitudinal, Multimodal MRI Study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;47(4):995-1007. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150196. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 26401778
-
Adiposity is related to cerebrovascular and brain volumetry outcomes in the RUN DMC study.Neurology. 2019 Aug 27;93(9):e864-e878. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008002. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Neurology. 2019. PMID: 31363056
Cited by
-
Hot Topics in Research: Preventive Neuroradiology in Brain Aging and Cognitive Decline.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015 Oct;36(10):1803-9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4409. Epub 2015 Jun 4. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 26045577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Brain Structure and Cognition Following Bariatric Surgery.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Feb 5;7(2):e2355380. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.55380. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38334996 Free PMC article.
-
Brain volume, energy balance, and cardiovascular health in two nonindustrial South American populations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Mar 28;120(13):e2205448120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2205448120. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36940322 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms linking obesity and its metabolic comorbidities with cerebral grey and white matter changes.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022 Aug;23(4):833-843. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09706-5. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 35059979 Review.
-
Obesity as a Risk Factor for Accelerated Brain Ageing in First-Episode Psychosis-A Longitudinal Study.Schizophr Bull. 2021 Oct 21;47(6):1772-1781. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbab064. Schizophr Bull. 2021. PMID: 34080013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baskin M, Ard J, Franklin F, Allison D (2005): Prevalence of obesity in the United States. Obesity Rev 6:5–7. - PubMed
-
- Considine R, Sinha M, Heiman M, Kriauciunas A, Stephens T, Nyce M, Ohannesian J, Marco C, McKee L, Bauer T (1996): Serum immunoreactive‐leptin concentrations in normal‐weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 334:292–295. - PubMed
-
- Cournot M, Marquie J, Ansiau D, Martinaud C, Fonds H, Ferrieres J, Ruidavets J (2006): Relation between body mass index and cognitive function in healthy middle‐aged men and women. Neurology 67:1208–1214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

