Anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects of tadalafil in diabetic mice
- PMID: 23028874
- PMCID: PMC3448606
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045243
Anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects of tadalafil in diabetic mice
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance impairs nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability and obesity promotes a state of chronic inflammation and damages the vascular endothelium. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors restore NO signaling and may reduce circulating inflammatory markers, and improve metabolic parameters through a number of mechanisms. We hypothesized that daily administration of the PDE-5 inhibitor, tadalafil (TAD) will attenuate inflammation, improve fasting plasma glucose and triglyceride levels, body weight, and reduce infarct size after ischemia/reperfusion injury in obese, diabetic mice.
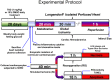
Methods: Twenty leptin receptor null (db/db) mice underwent treatment with TAD (1 mg/Kg) or 10% DMSO for 28 days. Body weight and fasting plasma glucose levels were determined weekly. Upon completion, hearts were isolated and subjected to 30 min global ischemia followed by 60 min reperfusion in a Langendorff model. Plasma samples were taken for cytokine analysis and fasting triglyceride levels. Infarct size was measured using computer morphometry of tetrazolium stained sections. Additionally, ventricular cardiomyocytes were isolated and subjected to 40 min of simulated ischemia and reoxygenation. Necrosis was determined using trypan blue exclusion and LDH release assay and apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL assay after 1 h or 18 h of reoxygenation, respectively.
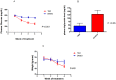
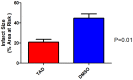
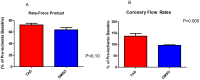
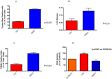
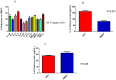
Results: Treatment with TAD caused a reduction in infarct size in the diabetic heart (23.2 ± 1.5 vs. 47.8 ± 3.7%, p<0.01, n = 6/group), reduced fasting glucose levels (292 ± 31.8 vs. 511 ± 19.3 mg/dL, p<0.001) and fasting triglycerides (43.3 ± 21 vs. 129.7 ± 29 mg/dL, p<0.05) as compared to DMSO, however body weight was not significantly reduced. Circulating tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β were reduced after treatment compared to control (257 ± 16.51 vs. 402.3 ± 17.26 and 150.8 ± 12.55 vs. 264 ± 31.85 pg/mL, respectively; P<0.001) Isolated cardiomyocytes from TAD-treated mice showed reduced apoptosis and necrosis.
Conclusion: We have provided the first evidence that TAD therapy ameliorates circulating inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in a diabetic animal model while improving fasting glucose levels and reducing infarct size following ischemia-reperfusion injury in the heart.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor tadalafil attenuates oxidative stress and protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetic mice.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Jul;60:80-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.031. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23385031
-
Chronic inhibition of phosphodiesterase 5 with tadalafil affords cardioprotection in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome: role of nitric oxide.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 May;468(1-2):47-58. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03710-0. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32162053 Free PMC article.
-
PDE5 Inhibitor Tadalafil and Hydroxychloroquine Cotreatment Provides Synergistic Protection against Type 2 Diabetes and Myocardial Infarction in Mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017 Apr;361(1):29-38. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.239087. Epub 2017 Jan 25. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017. PMID: 28123046 Free PMC article.
-
Treating diabetes with combination of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors and hydroxychloroquine-a possible prevention strategy for COVID-19?Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Mar;478(3):679-696. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04520-2. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36036333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin ameliorates myocardial infarction in obese diabetic individuals: The possible involvement of macrophage apoptotic factors.J Pineal Res. 2023 Mar;74(2):e12847. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12847. Epub 2022 Dec 8. J Pineal Res. 2023. PMID: 36456538 Review.
Cited by
-
PDE5 inhibitor potentially improves polyuria and bladder storage and voiding dysfunctions in type 2 diabetic rats.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 18;19(9):e0301883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301883. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39292699 Free PMC article.
-
Tadalafil versus pentoxifylline in the management of diabetic kidney disease: a randomized clinical trial.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Jun 24;16(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01363-3. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38915115 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase in heart and vessels: from physiology to diseases.Physiol Rev. 2024 Apr 1;104(2):765-834. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37971403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy of PDE5 inhibitors in diabetic patients.Andrology. 2023 Feb;11(2):245-256. doi: 10.1111/andr.13328. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Andrology. 2023. PMID: 36367281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of low-dose tadalafil once daily on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and erectile dysfunction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022 Apr 21;14(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00825-w. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 35449082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The American Diabetes Association- diabetes statistics website. Available: http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/diabetes-statistics/. Accessed: 2012 August 3.
-
- Ayala JE, Bracy DP, Julien BM, Rottman JN, Fueger PT, et al. (2007) Chronic treatment with sildenafil improves energy balance and insulin action in high-fat-fed conscious mice. Diabetes 57: 1025–1033. - PubMed
-
- Deyoung L, Chung E, Kovac JR, Romano W, Brock GB (2012) Daily use of sildenafil improves endothelial function in men with type 2 diabetes. J Androl 33: 176–180. - PubMed
-
- Wen Y, Skidmore JC, Porter-Turner MM, Rea CA, Khokher MA, et al. (2002) Relationship of glycation, antioxidant status and oxidative stress to vascular damage in diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 4: 305–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

