Knockout of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor impairs distal lung morphogenesis
- PMID: 23139760
- PMCID: PMC3491012
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048071
Knockout of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor impairs distal lung morphogenesis
Abstract
Background: Insulin-like growth factors (IGF-I and -II) are pleiotropic regulators of somatic growth and development in vertebrate species. Endocrine and paracrine effects of both hormones are mediated by a common IGF type 1 receptor (IGF-1R). Lethal respiratory failure in neonatal IGF-1R knockout mice suggested a particular role for this receptor in pulmonary development, and we therefore investigated the consequences of IGF-1R inactivation in lung tissue.
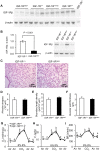
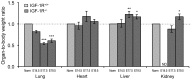
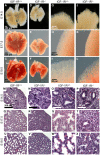
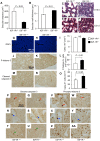
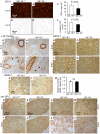
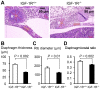
Methods and findings: We first generated compound heterozygous mutant mice harboring a hypomorphic (Igf1r(neo)) and a null (Igf1r(-)) allele. These IGF-1R(neo/-) mice express only 22% of normal IGF-1R levels and are viable. In adult IGF-1R(neo/-) mice, we assessed lung morphology and respiratory physiology and found normal histomorphometric characteristics and normal breathing response to hypercapnia. We then generated homozygous IGF-1R knockout mutants (IGF-1R(-/-)) and analyzed their lung development during late gestation using histomorphometric and immunohistochemical methods. IGF-1R(-/-) embryos displayed severe lung hypoplasia and markedly underdeveloped diaphragms, leading to lethal neonatal respiratory distress. Importantly, IGF-1R(-/-) lungs from late gestation embryos were four times smaller than control lungs and showed markedly thickened intersaccular mesenchyme, indicating strongly delayed lung maturation. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were significantly increased in IGF-1R(-/-) lung tissue as compared with IGF-1R(+/+) controls. Immunohistochemistry using pro-SP-C, NKX2-1, CD31 and vWF as markers revealed a delay in cell differentiation and arrest in the canalicular stage of prenatal respiratory organ development in IGF-1R(-/-) mutant mice.
Conclusions/significance: We found that low levels of IGF-1R were sufficient to ensure normal lung development in mice. In contrast, complete absence of IGF-1R significantly delayed end-gestational lung maturation. Results indicate that IGF-1R plays essential roles in cell proliferation and timing of cell differentiation during fetal lung development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deficiency in type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor in mice protects against oxygen-induced lung injury.Respir Res. 2005 Apr 8;6(1):31. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-31. Respir Res. 2005. PMID: 15819984 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis in prenatal IGF1-deficient mice identifies molecular pathways and _target genes involved in distal lung differentiation.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 31;8(12):e83028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083028. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24391734 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling regulates skin development and inhibits skin keratinocyte differentiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(7):2675-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.7.2675-2687.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16537911 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Igf1r in Bronchiolar Epithelial Regeneration: Role during Repair Kinetics after Selective Club Cell Ablation.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 18;11(11):e0166388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166388. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27861515 Free PMC article.
-
[Physiology of somatotropic axis: interest of gene inactivation experiments].Bull Acad Natl Med. 2003;187(7):1225-43; discussion 1244-7. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2003. PMID: 15146601 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Sheep recombinant IGF-1 promotes organ-specific growth in fetal sheep.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 25;13:954948. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.954948. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36091374 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Signaling in Lung Development and Inflammatory Lung Diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jun 19;2018:6057589. doi: 10.1155/2018/6057589. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30018981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF1R Deficiency Modulates Brain Signaling Pathways and Disturbs Mitochondria and Redox Homeostasis.Biomedicines. 2021 Feb 6;9(2):158. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020158. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33562061 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Type 1 Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Encephalopathy.Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:626019. doi: 10.1155/2015/626019. Epub 2015 May 18. Int J Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26089889 Free PMC article.
-
rhIGF-1/BP3 Preserves Lung Growth and Prevents Pulmonary Hypertension in Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 May 1;201(9):1120-1134. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201910-1975OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32101461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 75: 59–72. - PubMed
-
- Pichel JG, Fernández-Moreno C, Vicario-Abejón C, Testillano PS, Patterson PH, et al. (2003) Developmental cooperation of leukemia inhibitory factor and insulin-like growth factor I in mice is tissue-specific and essential for lung maturation involving the transcription factors Sp3 and TTF-1. Mech Dev 120: 349–361. - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Barriuso N, López-Malpartida AV, de Pablo F, Pichel JG (2006) Alterations in alveolar epithelium differentiation and vasculogenesis in lungs of LIF/IGF-I double deficient embryos. Dev Dyn 235: 2040–2050. - PubMed
-
- Silva D, Venihaki M, Guo WH, Lopez MF (2006) Igf2 deficiency results in delayed lung development at the end of gestation. Endocrinology 147: 5584–5591. - PubMed
-
- Nagata K, Masumoto K, Uesugi T, Yamamoto S, Yoshizaki K, et al. (2007) Effect of insulin-like-growth factor and its receptors regarding lung development in fetal mice. Pediatr Surg Int 10: 953–959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

