Agriculture Policy Is Health Policy
- PMID: 23144677
- PMCID: PMC3489137
- DOI: 10.1080/19320240903321367
Agriculture Policy Is Health Policy
Abstract
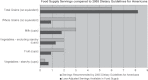
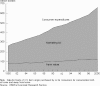
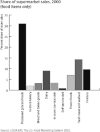
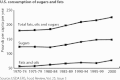
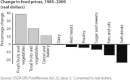
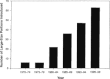
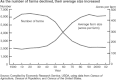
The Farm Bill is meant to supplement and secure farm incomes, ensure a stable food supply, and support the American farm economy. Over time, however, it has evolved into a system that creates substantial health impacts, both directly and indirectly. By generating more profit for food producers and less for family farmers; by effectively subsidizing the production of lower-cost fats, sugars, and oils that intensify the health-destroying obesity epidemic; by amplifying environmentally destructive agricultural practices that impact air, water, and other resources, the Farm Bill influences the health of Americans more than is immediately apparent. In this article, we outline three major public health issues influenced by American farm policy. These are (1) rising obesity; (2) food safety; and (3) environmental health impacts, especially exposure to toxic substances and pesticides.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Agricultural policy and childhood obesity: a food systems and public health commentary.Health Aff (Millwood). 2010 Mar-Apr;29(3):405-10. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2010.0102. Health Aff (Millwood). 2010. PMID: 20194980
-
On the choice of farm management practices after the reform of the Common Agricultural Policy in 2003.J Environ Manage. 2007 Feb;82(3):332-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.12.027. Epub 2006 Nov 13. J Environ Manage. 2007. PMID: 17095138
-
Pesticide use and practices in an Iowa farm family pesticide exposure study.J Agric Saf Health. 2002 Nov;8(4):423-33. doi: 10.13031/2013.10222. J Agric Saf Health. 2002. PMID: 12549246
-
Agricultural subsidies and the American obesity epidemic.Am J Prev Med. 2013 Sep;45(3):327-33. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2013.04.010. Am J Prev Med. 2013. PMID: 23953360 Review.
-
Occupational exposure to pesticides and associated health effects among greenhouse farm workers.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jun;27(18):22251-22270. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08754-9. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32333353 Review.
Cited by
-
Policy gaps and food systems optimization: a review of agriculture, environment, and health policies in South Africa.Front Sustain Food Syst. 2023 Aug 17;7:867481. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.867481. Front Sustain Food Syst. 2023. PMID: 37693217 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of Obesity and Diabetes and Their Cardiovascular Complications.Circ Res. 2016 May 27;118(11):1723-35. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306825. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27230638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reproductive health and the industrialized food system: a point of intervention for health policy.Health Aff (Millwood). 2011 May;30(5):888-97. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2010.1255. Health Aff (Millwood). 2011. PMID: 21555472 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of neighborhood food stores on change in young girls' body mass index.Am J Prev Med. 2011 Jul;41(1):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2011.03.013. Am J Prev Med. 2011. PMID: 21665062 Free PMC article.
-
Future of farming must be food not tobacco.Tob Control. 2023 May;32(3):269-270. doi: 10.1136/tc-2023-058004. Tob Control. 2023. PMID: 37080585 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wang Y, Beydoun MA. The obesity epidemic in the United States—gender, age, socioeconomic, racial/ethnic, and geographic characteristics: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 2007;29:6, 28. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Fact Sheet: General Information and National Estimates on Diabetes in the United States, 2005. Atlanta, Ga: US Dept of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2005.
-
- Narayan KMV, Boyle JP, Thompson TJ, Sorensen SW, Williamson DF. Lifetime risk for diabetes mellitus in the United States. JAMA. 2003;290:1884, 1890. - PubMed
-
- Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, et al. A potential decline in life expectancy in the United States in the 21st century. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1138, 1145. - PubMed
-
- Popkin BM, Kim S, Rusev ER, Du S, Zizza, C. Measuring the full economic costs of diet, physical activity and obesity-related chronic diseases. Obes Rev. 2006;7:271, 293. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
