Group VIB Phospholipase A(2) promotes proliferation of INS-1 insulinoma cells and attenuates lipid peroxidation and apoptosis induced by inflammatory cytokines and oxidant agents
- PMID: 23213352
- PMCID: PMC3503447
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/989372
Group VIB Phospholipase A(2) promotes proliferation of INS-1 insulinoma cells and attenuates lipid peroxidation and apoptosis induced by inflammatory cytokines and oxidant agents
Abstract
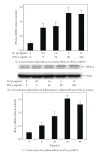
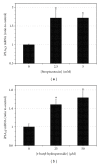
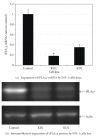
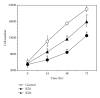
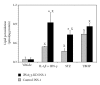
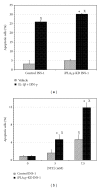
Group VIB Phospholipase A(2) (iPLA(2)γ) is distributed in membranous organelles in which β-oxidation occurs, that is, mitochondria and peroxisomes, and is expressed by insulin-secreting pancreatic islet β-cells and INS-1 insulinoma cells, which can be injured by inflammatory cytokines, for example, IL-1β and IFN-γ, and by oxidants, for example, streptozotocin (STZ) or t-butyl-hydroperoxide (TBHP), via processes pertinent to mechanisms of β-cell loss in types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus. We find that incubating INS-1 cells with IL-1β and IFN-γ, with STZ, or with TBHP causes increased expression of iPLA(2)γ mRNA and protein. We prepared INS-1 knockdown (KD) cell lines with reduced iPLA(2)γ expression, and they proliferate more slowly than control INS-1 cells and undergo increased membrane peroxidation in response to cytokines or oxidants. Accumulation of oxidized phospholipid molecular species in STZ-treated INS-1 cells was demonstrated by LC/MS/MS scanning, and the levels in iPLA(2)γ-KD cells exceeded those in control cells. iPLA(2)γ-KD INS-1 cells also exhibited higher levels of apoptosis than control cells when incubated with STZ or with IL-1β and IFN-γ. These findings suggest that iPLA(2)γ promotes β-cell proliferation and that its expression is increased during inflammation or oxidative stress as a mechanism to mitigate membrane injury that may enhance β-cell survival.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Studies of insulin secretory responses and of arachidonic acid incorporation into phospholipids of stably transfected insulinoma cells that overexpress group VIA phospholipase A2 (iPLA2beta ) indicate a signaling rather than a housekeeping role for iPLA2beta.J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 20;276(16):13198-208. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010423200. Epub 2001 Jan 22. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278673
-
Decreased iPLA2gamma expression induces lipid peroxidation and cell death and sensitizes cells to oxidant-induced apoptosis.J Lipid Res. 2008 Jul;49(7):1477-87. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800030-JLR200. Epub 2008 Apr 8. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18398221 Free PMC article.
-
Protection of pancreatic beta-cells by group VIA phospholipase A(2)-mediated repair of mitochondrial membrane peroxidation.Endocrinology. 2010 Jul;151(7):3038-48. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0016. Epub 2010 May 12. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20463052 Free PMC article.
-
Group VIA Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2beta) and its role in beta-cell programmed cell death.Biochimie. 2010 Jun;92(6):627-37. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 20083151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A link between endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced β-cell apoptosis and the group VIA Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2β).Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010 Oct;12 Suppl 2(0 2):93-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01270.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010. PMID: 21029305 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polarization of Macrophages toward M2 Phenotype Is Favored by Reduction in iPLA2β (Group VIA Phospholipase A2).J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 28;291(44):23268-23281. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.754945. Epub 2016 Sep 20. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27650501 Free PMC article.
-
High patatin like phospholipase domain containing 8 expression as a biomarker for poor prognosis of colorectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Mar 15;16(3):787-797. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.787. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38577466 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid-Stimulated Insulin Secretion vs. Lipotoxicity.Molecules. 2018 Jun 19;23(6):1483. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061483. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29921789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoprotective activity of mitochondrial uncoupling protein-2 in lung and spleen.FEBS Open Bio. 2018 Mar 12;8(4):692-701. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12410. eCollection 2018 Apr. FEBS Open Bio. 2018. PMID: 29632821 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-independent phospholipases A2 and their roles in biological processes and diseases.J Lipid Res. 2015 Sep;56(9):1643-68. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R058701. Epub 2015 May 28. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26023050 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leahy JL. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Archives of Medical Research. 2005;36(3):197–209. - PubMed
-
- Mathis D, Vence L, Benoist C. β-cell death during progression to diabetes. Nature. 2001;414(6865):792–798. - PubMed
-
- Gepts W. Pathologic anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1965;14(10):619–633. - PubMed
-
- Mandrup-Poulsen T. The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of IDDM. Diabetologia. 1996;39(9):1005–1029. - PubMed
-
- Rabinovitch A, Suarez-Pinzon WL. Cytokines and their roles in pancreatic islet β-cell destruction and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1998;55(8):1139–1149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

