Electroacupuncture suppresses mechanical allodynia and nuclear factor κ B signaling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 23230847
- PMCID: PMC6493446
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12035
Electroacupuncture suppresses mechanical allodynia and nuclear factor κ B signaling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Abstract
Aims: To investigate whether electroacupuncture (EA) produced analgesic effect and whether nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and cystathionine β synthase (CBS) involved in EA-mediated analgesia in painful diabetic neuropathy in rats.
Methods: Diabetes was induced by an intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ) in adult female rats. Mechanical pain threshold was measured by von Frey filaments. EA was applied at acupoint Zu-San-Li (ST-36) in both hindlimbs. Western blot analysis was employed to detect changes in protein levels of NF-κB and CBS in spinal dorsal root ganglion (DRGs).
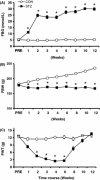
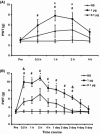
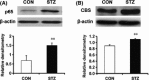
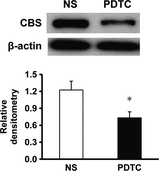
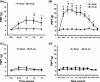
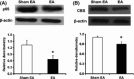
Results: Mechanical allodynia was developed 2 weeks after STZ injection and lasted for another 4 weeks. STZ injection significantly enhanced expression of p65 and CBS in lumbar L4-6 DRGs when compared with age-matched controls. EA markedly attenuated mechanical allodynia. Importantly, EA treatment remarkably inhibited p65 and CBS expression in DRGs. Additionally, intrathecal injection of the p65 antagonist pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuated mechanical allodynia and markedly inhibited CBS expression in DRGs in STZ rats.
Conclusions: These data indicate that EA produced an analgesic effect, which might be mediated at least in a part by inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway in primary sensory neurons in rats with diabetes.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoted interaction of nuclear factor-κB with demethylated cystathionine-β-synthetase gene contributes to gastric hypersensitivity in diabetic rats.J Neurosci. 2013 May 22;33(21):9028-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1068-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23699514 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on bone cancer pain in rat model: the role of peripheral P2X3 receptor.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):13-27. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09861-7. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35478452 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 upregulates CBS expression through NF-κB activation in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome with chronic visceral hypersensitivity.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 28;21(28):8615-28. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i28.8615. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26229403 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin attenuates diabetic neuropathic pain via AMPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in dorsal root ganglion of diabetic rats.Brain Res. 2021 Dec 1;1772:147663. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147663. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 34555415
-
Alpha-lipoic acid downregulates TRPV1 receptor via NF-κB and attenuates neuropathic pain in rats with diabetes.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020 Jul;26(7):762-772. doi: 10.1111/cns.13303. Epub 2020 Mar 16. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020. PMID: 32175676 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proteomics Analysis of the Spinal Dorsal Horn in Diabetic Painful Neuropathy Rats With Electroacupuncture Treatment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 10;12:608183. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.608183. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34177794 Free PMC article.
-
SMN deficiency causes pain hypersensitivity in a mild SMA mouse model through enhancing excitability of nociceptive dorsal root ganglion neurons.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 24;9(1):6493. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43053-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31019235 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase contributes to diabetic neuropathic pain through upregulation of toll-like receptor 4 in rats.Mol Pain. 2019 Jan-Dec;15:1744806919838659. doi: 10.1177/1744806919838659. Mol Pain. 2019. PMID: 30838902 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of CXCR4 through promoter demethylation contributes to inflammatory hyperalgesia in rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018 Oct;24(10):947-956. doi: 10.1111/cns.12845. Epub 2018 Mar 25. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018. PMID: 29577638 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Acupuncture on Diabetic Neuropathy: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 9;22(16):8575. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168575. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445280 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ross MA. Neuropathies associated with diabetes. Med Clin North Am 1993;77:111–124. - PubMed
-
- Dyck PJ, Kratz KM, Karnes JL, et al. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population‐based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 1993;43:817–824. - PubMed
-
- Khan GM, Chen SR, Pan HL. Role of primary afferent nerves in allodynia caused by diabetic neuropathy in rats. Neuroscience 2002;114:291–299. - PubMed
-
- Tu WZ, Cheng RD, Cheng B, et al. Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on chronic neuropathic pain mediated by P2X3 receptors in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurochem Int 2012;60:379–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

