Induction without methanol: novel regulated promoters enable high-level expression in Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 23347568
- PMCID: PMC3615954
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-5
Induction without methanol: novel regulated promoters enable high-level expression in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
Background: Inducible high-level expression is favoured for recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris. Therefore, novel regulated promoters are desired, ideally repressing heterologous gene expression during initial growth and enabling it in the production phase. In a typical large scale fed-batch culture repression is desired during the batch phase where cells grow on a surplus of e.g. glycerol, while heterologous gene expression should be active in the feed phase under carbon (e.g. glucose) limitation.
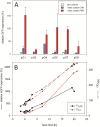
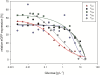
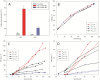
Results: DNA microarray analysis of P. pastoris wild type cells growing in glycerol-based batch and glucose-based fed batch was used for the identification of genes with both, strong repression on glycerol and high-level expression in the feed phase. Six novel glucose-limit inducible promoters were successfully applied to express the intracellular reporter eGFP. The highest expression levels together with strong repression in pre-culture were achieved with the novel promoters P(G1) and P(G6). Human serum albumin (HSA) was used to characterize the promoters with an industrially relevant secreted protein. A P(G1) clone with two gene copies reached about 230% of the biomass specific HSA titer in glucose-based fed batch fermentation compared to a P(GAP) clone with identical gene copy number, while P(G6) only achieved 39%. Two clones each carrying eleven gene copies, expressing HSA under control of P(G1) and P(G6) respectively were generated by post-transformational vector amplification. They produced about 1.0 and 0.7 g L(-1) HSA respectively in equal fed batch processes. The suitability in production processes was also verified with HyHEL antibody Fab fragment for P(G1) and with porcine carboxypeptidase B for P(G6). Moreover, the molecular function of the gene under the control of P(G1) was determined to encode a high-affinity glucose transporter and named GTH1.
Conclusions: A set of novel regulated promoters, enabling induction without methanol, was successfully identified by using DNA microarrays and shown to be suitable for high level expression of recombinant proteins in glucose-based protein production processes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomarkers allow detection of nutrient limitations and respective supplementation for elimination in Pichia pastoris fed-batch cultures.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Jul 11;16(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0730-9. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 28693509 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive clone screening and evaluation of fed-batch strategies in a microbioreactor and lab scale stirred tank bioreactor system: application on Pichia pastoris producing Rhizopus oryzae lipase.Microb Cell Fact. 2014 Mar 7;13(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-36. Microb Cell Fact. 2014. PMID: 24606982 Free PMC article.
-
Bioprocess and downstream optimization of recombinant bovine chymosin B in Pichia (Komagataella) pastoris under methanol-inducible AOXI promoter.Protein Expr Purif. 2014 Dec;104:85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Protein Expr Purif. 2014. PMID: 25278015
-
Fed-batch high-cell-density fermentation strategies for Pichia pastoris growth and production.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019 Mar;39(2):258-271. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2018.1554620. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30599783 Review.
-
Engineering strategies for enhanced production of protein and bio-products in Pichia pastoris: A review.Biotechnol Adv. 2018 Jan-Feb;36(1):182-195. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.11.002. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Biotechnol Adv. 2018. PMID: 29129652 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpressing _target helper genes enhances secretion and glycosylation of recombinant proteins in Pichia pastoris under simulated microgravity.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Oct;43(10):1429-39. doi: 10.1007/s10295-016-1817-8. Epub 2016 Aug 17. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27535143
-
Pichia pastoris Mut(S) strains are prone to misincorporation of O-methyl-L-homoserine at methionine residues when methanol is used as the sole carbon source.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 Jun 7;15:98. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0499-2. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 27267127 Free PMC article.
-
Integration event induced changes in recombinant protein productivity in Pichia pastoris discovered by whole genome sequencing and derived vector optimization.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 May 20;15:84. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0486-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 27206580 Free PMC article.
-
Current advances of Pichia pastoris as cell factories for production of recombinant proteins.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 24;13:1059777. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1059777. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36504810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and purification of recombinant G protein-coupled receptors: A review.Protein Expr Purif. 2020 Mar;167:105524. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2019.105524. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Protein Expr Purif. 2020. PMID: 31678667 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

