Kidney disease and increased mortality risk in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 23362314
- PMCID: PMC3559486
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012070718
Kidney disease and increased mortality risk in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
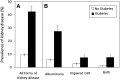
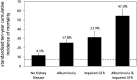
Type 2 diabetes associates with increased risk of mortality, but how kidney disease contributes to this mortality risk among individuals with type 2 diabetes is not completely understood. Here, we examined 10-year cumulative mortality by diabetes and kidney disease status for 15,046 participants in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) by linking baseline data from NHANES III with the National Death Index. Kidney disease, defined as urinary albumin/creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/g and/or estimated GFR ≤60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2), was present in 9.4% and 42.3% of individuals without and with type 2 diabetes, respectively. Among people without diabetes or kidney disease (reference group), 10-year cumulative all-cause mortality was 7.7% (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 7.0%-8.3%), standardized to population age, sex, and race. Among individuals with diabetes but without kidney disease, standardized mortality was 11.5% (95% CI, 7.9%-15.2%), representing an absolute risk difference with the reference group of 3.9% (95% CI, 0.1%-7.7%), adjusted for demographics, and 3.4% (95% CI, -0.3% to 7.0%) when further adjusted for smoking, BP, and cholesterol. Among individuals with both diabetes and kidney disease, standardized mortality was 31.1% (95% CI, 24.7%-37.5%), representing an absolute risk difference with the reference group of 23.4% (95% CI, 17.0%-29.9%), adjusted for demographics, and 23.4% (95% CI, 17.2%-29.6%) when further adjusted. We observed similar patterns for cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality. In conclusion, those with kidney disease predominantly account for the increased mortality observed in type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Temporal trends in the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease in the United States.JAMA. 2011 Jun 22;305(24):2532-9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.861. JAMA. 2011. PMID: 21693741 Free PMC article.
-
Albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate as predictors of diabetic end-stage renal disease and death.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Oct;6(10):2444-51. doi: 10.2215/CJN.00580111. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21852671 Free PMC article.
-
Non-albuminuric renal impairment is a strong predictor of mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: the Renal Insufficiency And Cardiovascular Events (RIACE) Italian multicentre study.Diabetologia. 2018 Nov;61(11):2277-2289. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4691-2. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30032426
-
Associations of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with mortality and renal failure by sex: a meta-analysis.BMJ. 2013 Jan 29;346:f324. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f324. BMJ. 2013. PMID: 23360717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney Disease in Diabetes.In: Cowie CC, Casagrande SS, Menke A, Cissell MA, Eberhardt MS, Meigs JB, Gregg EW, Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Becker DJ, Brancati FL, Boyko EJ, Herman WH, Howard BV, Narayan KMV, Rewers M, Fradkin JE, editors. Diabetes in America. 3rd edition. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (US); 2018 Aug. CHAPTER 22. In: Cowie CC, Casagrande SS, Menke A, Cissell MA, Eberhardt MS, Meigs JB, Gregg EW, Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Becker DJ, Brancati FL, Boyko EJ, Herman WH, Howard BV, Narayan KMV, Rewers M, Fradkin JE, editors. Diabetes in America. 3rd edition. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (US); 2018 Aug. CHAPTER 22. PMID: 33651560 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling of insulin-resistant kidney models and human biopsies reveals common and cell-type-specific mechanisms underpinning Diabetic Kidney Disease.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 19;15(1):10018. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54089-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39562547 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Renal Functions and Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Oct 17;16(10):e71739. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71739. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39553106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Dietary Flavonoids Intake With All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality in Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Cohort Study From the NHANES Database.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Nov 4;2024:8359294. doi: 10.1155/2024/8359294. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 39529845 Free PMC article.
-
The role of moderate to vigorous physical activity level and number of treatments/medications in mediating the effect of body mass index on diabetic nephropathy: a Mendelian randomization study.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2417738. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2417738. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39466707 Free PMC article.
-
The early diagnostic value of serum renalase level in diabetic kidney disease and diabetic macroangiopathy: a retrospective case-control study.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2024 Oct 16;15:20406223241286677. doi: 10.1177/20406223241286677. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2024. PMID: 39429975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization: Diabetes Fact Sheet, 2012. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/index.html Accessed September 12, 2012
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ: Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87: 4–14, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Seshasai SR, Kaptoge S, Thompson A, Di Angelantonio E, Gao P, Sarwar N, Whincup PH, Mukamal KJ, Gillum RF, Holme I, Njølstad I, Fletcher A, Nilsson P, Lewington S, Collins R, Gudnason V, Thompson SG, Sattar N, Selvin E, Hu FB, Danesh J, Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration : Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N Engl J Med 364: 829–841, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ninomiya T, Perkovic V, de Galan BE, Zoungas S, Pillai A, Jardine M, Patel A, Cass A, Neal B, Poulter N, Mogensen CE, Cooper M, Marre M, Williams B, Hamet P, Mancia G, Woodward M, Macmahon S, Chalmers J, ADVANCE Collaborative Group : Albuminuria and kidney function independently predict cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 20: 1813–1821, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

