A common MicroRNA signature consisting of miR-133a, miR-139-3p, and miR-142-3p clusters bladder carcinoma in situ with normal umbrella cells
- PMID: 23410519
- PMCID: PMC3620415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.01.006
A common MicroRNA signature consisting of miR-133a, miR-139-3p, and miR-142-3p clusters bladder carcinoma in situ with normal umbrella cells
Abstract
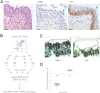
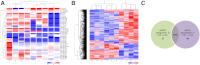
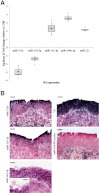
miRNAs are small noncoding RNAs with critical roles in a large variety of biological processes such as development and tumorigenesis. miRNA expression profiling has been reported to be a powerful tool to classify tissue samples, including cancers, based on their developmental lineage. In this study, we have profiled the expression of miRNAs in bladder carcinoma in situ (CIS) and distinct cell compartments of the normal bladder, namely umbrella and basal-intermediate urothelial cells, as well as the muscularis propria. We identified several miRNAs differentially expressed between umbrella and basal-intermediate cells (miR-133a, miR-139-3p, miR-142-3p, miR-199b-5p, and miR-221). In situ hybridization confirmed the expression of miR-133a and miR-139-3p in umbrella cells, and miR-142-3p in basal-intermediate cells. Strikingly, miRNA expression levels of CIS most closely resembled the miRNA profile of umbrella cells. Finally, we examined well-established umbrella and basal-intermediate cell immunohistochemical biomarkers in an independent series of CIS samples. Again, this analysis revealed the significant expression of umbrella-specific markers in CIS when compared to non-CIS lesions. Overall, our studies represent a comprehensive and accurate description of the different miRNAs expressed in CIS tumors and three distinct histological areas of the urinary bladder. Notably, this study provides evidence of the possible origin relationship between CIS and normal umbrella cells.
Copyright © 2013 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Panel of MicroRNA Signature as a Tool for Predicting Survival of Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder.Dis Markers. 2018 Jun 20;2018:5468672. doi: 10.1155/2018/5468672. eCollection 2018. Dis Markers. 2018. PMID: 30026881 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA expression profile in a large series of bladder tumors: identification of a 3-miRNA signature associated with aggressiveness of muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Int J Cancer. 2013 Jun 1;132(11):2479-91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27949. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23169479
-
MicroRNA signature for estimating the survival time in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 9;12(1):4141. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08082-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35264666 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of microRNAs in bladder cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2013 Jul;10(7):396-404. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2013.113. Epub 2013 May 28. Nat Rev Urol. 2013. PMID: 23712207 Review.
-
Diagnostic value of microRNAs in asbestos exposure and malignant mesothelioma: systematic review and qualitative meta-analysis.Onco_target. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58606-58637. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.9686. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 27259231 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High miR-139-3p expression predicts a better prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: a pooled analysis.J Int Med Res. 2019 Jan;47(1):383-390. doi: 10.1177/0300060518802727. Epub 2018 Nov 5. J Int Med Res. 2019. PMID: 30394818 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in miRNA expression in early stage lung adenocarcinomas that did and did not relapse.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 16;9(7):e101802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101802. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25028925 Free PMC article.
-
Silenced lncRNA SNHG14 restrains the biological behaviors of bladder cancer cells via regulating microRNA-211-3p/ESM1 axis.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Jan 22;21(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01717-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33482820 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-139-5p: promising biomarker for cancer.Tumour Biol. 2015 Mar;36(3):1355-65. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3199-3. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25691250 Review.
-
Downregulation of long noncoding RNA TUG1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through the TUG1/miR-142/ZEB2 axis in bladder cancer cells.Onco _targets Ther. 2017 May 5;10:2461-2471. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S124595. eCollection 2017. Onco _targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28503069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu X.R., Lin J.H., Walz T., Haner M., Yu J., Aebi U., Sun T.T. Mammalian uroplakins. A group of highly conserved urothelial differentiation-related membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:13716–13724. - PubMed
-
- Harnden P., Eardley I., Joyce A.D., Southgate J. Cytokeratin 20 as an objective marker of urothelial dysplasia. Br J Urol. 1996;78:870–875. - PubMed
-
- Sheinfeld J., Reuter V.E., Fair W.R., Cordon-Cardo C. Expression of blood group antigens in bladder cancer: current concepts. Semin Surg Oncol. 1992;8:308–815. - PubMed
-
- Di Como C.J., Urist M.J., Babayan I., Drobnjak M., Hedvat C.V., Teruya-Feldstein J., Pohar K., Hoos A., Cordon-Cardo C. p63 expression profiles in human normal and tumor tissues. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:494–501. - PubMed
-
- Castillo-Martin M., Domingo-Domenech J., Karni-Schmidt O., Matos T., Cordon-Cardo C. Molecular pathways of urothelial development and bladder tumorigenesis. Urol Oncol. 2010;28:401–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

