Activation of the homeostatic intracellular repair response during cardiac surgery
- PMID: 23415552
- PMCID: PMC3724756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.12.034
Activation of the homeostatic intracellular repair response during cardiac surgery
Abstract
Background: The homeostatic intracellular repair response (HIR2) is an endogenous beneficial pathway that eliminates damaged mitochondria and dysfunctional proteins in response to stress. The underlying mechanism is adaptive autophagy. The purpose of this study was to determine whether the HIR2 response is activated in the heart in patients undergoing cardiac surgery and to assess whether it is associated with the duration of ischemic arrest and predicted surgical outcomes.
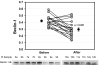
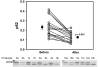
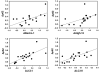
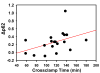
Study design: Autophagy was assessed in 19 patients undergoing coronary artery bypass or valve surgery requiring cardiopulmonary bypass. Biopsies of the right atrial appendage obtained before initiation of cardiopulmonary bypass and after weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass were analyzed for autophagy by immunoblotting for LC3, Beclin-1, autophagy 5-12, and p62. Changes in p62, a marker of autophagic flux, were correlated with duration of ischemia and with the mortality/morbidity risk scores obtained from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Adult Cardiac Surgery Database (version 2.73).
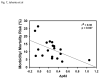
Results: Heart surgery was associated with a robust increase in autophagic flux indicated by depletion of LC3-I, LC3-II, Beclin-1, and autophagy 5-12; the magnitude of change for each of these factors correlated significantly with changes in the flux marker p62. In addition, changes in p62 correlated directly with cross-clamp time and inversely with the mortality and morbidity risk scores.
Conclusions: These findings are consistent with preclinical studies indicating that HIR2 is cardioprotective and reveal that it is activated in patients in response to myocardial ischemic stress. Strategies designed to amplify HIR2 during conditions of cardiac stress might have a therapeutic use and represent an entirely new approach to myocardial protection in patients undergoing heart surgery.
Copyright © 2013. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aortic and mitral valve surgery on the beating heart is lowering cardiopulmonary bypass and aortic cross clamp time.Heart Surg Forum. 2002;5(2):182-6. Heart Surg Forum. 2002. PMID: 12125670
-
Hydrogen sulfide protects against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by activating AMP-activated protein kinase to restore autophagic flux.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Mar 13;458(3):632-638. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25684185
-
The spectrum of myocardial homeostasis mechanisms in the settings of cardiac surgery procedures (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2018 Feb;17(2):2089-2099. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8174. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29207125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Choline Inhibits Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Cardiomyocyte Autophagy in Rat Myocardium by Activating Akt/mTOR Signaling.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(5):2136-2144. doi: 10.1159/000488049. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29533930
-
High LC3/Beclin Expression Correlates with Poor Survival in Glioma: a Definitive Role for Autophagy as Evidenced by In Vitro Autophagic Flux.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019 Jan;25(1):137-148. doi: 10.1007/s12253-017-0310-7. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 29022195
Cited by
-
Salvianolic acid B induced upregulation of miR-30a protects cardiac myocytes from ischemia/reperfusion injury.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Sep 1;16(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1275-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27586425 Free PMC article.
-
No evidence for activated autophagy in left ventricular myocardium at early reperfusion with protection by remote ischemic preconditioning in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting.PLoS One. 2014 May 5;9(5):e96567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096567. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24797938 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition).Autophagy. 2016;12(1):1-222. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1100356. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 26799652 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Management of ROS and Regulatory Cell Death in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 9. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01173-y. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38852121 Review.
-
Differential effects of atorvastatin on autophagy in ischemic and nonischemic myocardium in Ossabaw swine with metabolic syndrome.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014 Dec;148(6):3172-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.07.104. Epub 2014 Aug 13. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 25240527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayat H, Swaney JS, Ander AN, Dalton N, Kennedy BP, Hammond HK, et al. Progressive heart failure after myocardial infarction in mice. Basic Res Cardiol. 2002;97:206–13. - PubMed
-
- Cao CM, Xia Q, Gao Q, Chen M, Wong TM. Calcium-Activated Potassium Channel Triggers Cardioprotection of Ischemic Preconditioning. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2005;312:644–50. - PubMed
-
- Salloum FN, Takenoshita Y, Ockaili RA, Daoud VP, Chou E, Yoshida Ki, et al. Sildenafil and vardenafil but not nitroglycerin limit myocardial infarction through opening of mitochondrial KATP channels when administered at reperfusion following ischemia in rabbits. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2007;42:453–8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

