Aerobic fitness and intra-individual variability of neurocognition in preadolescent children
- PMID: 23511845
- PMCID: PMC3632076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandc.2013.02.006
Aerobic fitness and intra-individual variability of neurocognition in preadolescent children
Abstract
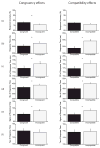
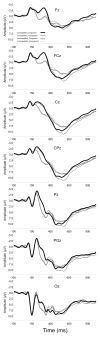
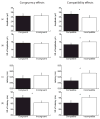
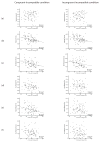
This study examined behavioral and neuroelectric intra-individual variability (IIV) in preadolescent children during a task requiring variable amounts of cognitive control. The current study further examined whether IIV was moderated by aerobic fitness level. Participants performed a modified flanker task, comprised of congruent and incongruent arrays, within compatible and incompatible stimulus-response conditions. Results revealed that congruent, relative to incongruent, conditions were associated with less IIV of RT. Further, less IIV of RT, P3 amplitude, and P3 latency was observed for the compatible relative to the incompatible condition. Higher fitness was associated with shorter and less variable RT only for the incompatible condition, with no fitness-related differences observed for P3 variability. The findings suggest that conditions requiring greater cognitive control are associated with increased IIV, and that higher fitness may be associated with greater integrity of cognitive control systems during development.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiorespiratory fitness and the flexible modulation of cognitive control in preadolescent children.J Cogn Neurosci. 2011 Jun;23(6):1332-45. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2010.21528. Epub 2010 Jun 3. J Cogn Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20521857
-
Aerobic fitness and cognitive development: Event-related brain potential and task performance indices of executive control in preadolescent children.Dev Psychol. 2009 Jan;45(1):114-29. doi: 10.1037/a0014437. Dev Psychol. 2009. PMID: 19209995
-
Acute exercise facilitates brain function and cognition in children who need it most: an ERP study of individual differences in inhibitory control capacity.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2014 Jan;7:53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24309300 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic fitness and response variability in preadolescent children performing a cognitive control task.Neuropsychology. 2011 May;25(3):333-41. doi: 10.1037/a0022167. Neuropsychology. 2011. PMID: 21443340 Free PMC article.
-
The relation of childhood physical activity and aerobic fitness to brain function and cognition: a review.Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2014 May;26(2):138-46. doi: 10.1123/pes.2013-0125. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2014. PMID: 24722921 Review.
Cited by
-
Adiposity influences intraindividual variability in behavioral and neuroelectric indices of attentional inhibition.Psychophysiology. 2024 Dec;61(12):e14677. doi: 10.1111/psyp.14677. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Psychophysiology. 2024. PMID: 39215400 Free PMC article.
-
Self-reported free-living physical activity and executive control in young adults.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 26;13(12):e0209616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209616. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30586447 Free PMC article.
-
Exposing an "Intangible" Cognitive Skill among Collegiate Football Players: Enhanced Interference Control.Front Psychol. 2018 Feb 9;9:49. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00049. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29479325 Free PMC article.
-
Variability in Executive Control Performance Is Predicted by Physical Activity.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Jan 21;13:463. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00463. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32038199 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity to cognitive processing in adolescents: findings from the ALSPAC birth cohort.Psychol Res. 2015 Sep;79(5):715-28. doi: 10.1007/s00426-014-0612-2. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Psychol Res. 2015. PMID: 25351943
References
-
- American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. 7. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; New York, NY: 2006.
-
- Albinet CT, Boucard G, Bouguet CA, Audiffren M. Increased heart rate variability and executive performance after aerobic training in the elderly. Eur J Appl Physio. 2010;109:617–624. - PubMed
-
- Anderson MC, Green C. Suppressing unwanted memories by executive control. Letters to Nature. 2001;410:366–369. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Or O. Pediatric sports medicine for the practitioner: From physiologic principles to clinical applications. Springer-Verlag; New York, NY: 1983.
-
- Birnbaum AS, Lytle LA, Murray DM, Story M, Perry CL, Boutelle KN. Survey development for assessing correlates of young adolescents’ eating. Am J Health Behav. 2002;26:284–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

