Effect of enamel matrix derivative on bone formation around intraosseous titanium implant: An experimental study in canine model
- PMID: 23559960
- PMCID: PMC3612232
Effect of enamel matrix derivative on bone formation around intraosseous titanium implant: An experimental study in canine model
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to perform a histological, histomorphometrical, and immunohistochemical evaluation of the effect of Enamel matrix derivative (EMD) on bone formation around titanium dental implant.
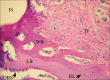
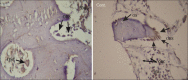
Materials and methods: In this animal study, 12 implants (10 × 3.8 mm) were inserted in the tibia bone of three dogs of Iranian breed. Two implants were placed in each tibia with EMD only on the left side. The dogs were sacrificed 2, 4, and 6 weeks after implantation. Following decalcification of the implants' surrounding tissue and preparation of 4 μm thick sections, they were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) and immunohistochemical (IHC) stain for osteopontin (OPN) marker. Histomorphometric evaluation was performed via measurement of the percentage of the woven, lamellar, and total generated bone. Light microscopy osteoblastic intensity of OPN in osteoblasts and bone matrix was also evaluated Data were analyzed by Wilcoxon signed Ranks, and Mc Nemar tests.
Results: In both control and EMD-applied groups, bone formation was recognized around the implants at the 4(th) week postimplantation. The percentage of total generated bone in the test group was higher than the control group, although being not statistically significant (P value = 0.917). Osteoclasts exhibited significantly higher proliferation activity compared the control group when stimulated by EMD (P value = 0.027). On average, the staining intensity in osteoblasts and extracellular matrix of bone, in EMD-applied subjects was higher than those of the controls (P value = 0.167 and P value = 0.414, respectively).
Conclusion: EMD enhanced bone formation around dental implants, but this increase was not significant.
Keywords: Bone formation; dental implant; enamel matrix protein; osteopontin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Applications of Enamel Matrix Derivative in Implant Dentistry: A Narrative Review.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jun 3;14(11):3045. doi: 10.3390/ma14113045. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enamel matrix derivative and bone healing after guided bone regeneration in dehiscence-type defects around implants. A histomorphometric study in dogs.J Periodontol. 2002 Jul;73(7):789-96. doi: 10.1902/jop.2002.73.7.789. J Periodontol. 2002. PMID: 12146539
-
Enamel matrix derivative and titanium implants.J Clin Periodontol. 2003 Apr;30(4):359-63. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051x.2003.00326.x. J Clin Periodontol. 2003. PMID: 12694436
-
Influence of biphasic calcium phosphate surfaces coated with Enamel Matrix Derivative on vertical bone growth in an extra-oral rabbit model.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016 Oct;27(10):1297-1304. doi: 10.1111/clr.12740. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016. PMID: 26689728
-
The effect of enamel matrix derivative (Emdogain) on bone formation: a systematic review.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2009 Sep;15(3):215-24. doi: 10.1089/ten.teb.2008.0065. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2009. PMID: 18710336 Review.
Cited by
-
The Applications of Enamel Matrix Derivative in Implant Dentistry: A Narrative Review.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jun 3;14(11):3045. doi: 10.3390/ma14113045. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enamel matrix derivative enhances the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells on the titanium implant surface.Organogenesis. 2017 Jul 3;13(3):103-113. doi: 10.1080/15476278.2017.1331196. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Organogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28598248 Free PMC article.
-
Enamel matrix derivative improves gingival fibroblast cell behavior cultured on titanium surfaces.Clin Oral Investig. 2016 May;20(4):685-95. doi: 10.1007/s00784-015-1558-5. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Clin Oral Investig. 2016. PMID: 26269319
References
-
- Schwartz-Arad D, Laviv A, Levin L. Failure causes, timing, and cluster behavior: An 8-year study of dental implants. Implant Dent. 2008;17:200–7. - PubMed
-
- Sakka S, Coulthard P. Implant failure: Etiology and complications. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011;16:42–4. - PubMed
-
- Schilephake H. Bone growth factors in maxillofacial skeletal reconstruction. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;31:469–84. - PubMed
-
- Van der Pauw MT, Van den Bos T, Everts V, Beertsen W. Enamel matrix-derivedprotein stimulates attachment of periodontal ligament fibroblasts and enhances alkaline phosphatase activity and transforming growth factorbeta1 release of periodontal ligament and gingival fibroblasts. J Periodontol. 2000;71:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Heijl L. Periodontal regeneration with enamel matrix derivative in one human experimental defect. A case report. J Clin Periodontol. 1997;24:693–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
