Autophagy modulation as a _target for anticancer drug discovery
- PMID: 23564085
- PMCID: PMC4002878
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2013.23
Autophagy modulation as a _target for anticancer drug discovery
Abstract
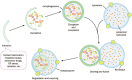
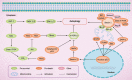
Autophagy, an evolutionarily conserved catabolic process involving the engulfment and degradation of non-essential or abnormal cellular organelles and proteins, is crucial for homeostatic maintenance in living cells. This highly regulated, multi-step process has been implicated in diverse diseases including cancer. Autophagy can function as either a promoter or a suppressor of cancer, which makes it a promising and challenging therapeutic _target. Herein, we overview the regulatory mechanisms and dual roles of autophagy in cancer. We also describe some of the representative agents that exert their anticancer effects by regulating autophagy. Additionally, some emerging strategies aimed at modulating autophagy are discussed as having the potential for future anticancer drug discovery. In summary, these findings will provide valuable information to better utilize autophagy in the future development of anticancer therapeutics that meet clinical requirements.
Figures
Similar articles
-
_targeting autophagy to overcome drug resistance in cancer therapy.Future Med Chem. 2015 Aug;7(12):1535-42. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.88. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Future Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26334206 Review.
-
Pharmacological inhibitors of autophagy as novel cancer therapeutic agents.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Mar;105:164-75. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.01.028. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 26826398 Review.
-
Interaction of autophagy with microRNAs and their potential therapeutic implications in human cancers.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt B):332-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.039. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25304373 Review.
-
Mechanisms of autophagy and relevant small-molecule compounds for _targeted cancer therapy.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 May;75(10):1803-1826. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2759-2. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29417176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy and chemotherapy resistance: a promising therapeutic _target for cancer treatment.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Oct 10;4(10):e838. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.350. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24113172 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emodin-induced autophagy against cell apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in human hepatocytes.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Sep 3;13:3171-3180. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S204958. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31564833 Free PMC article.
-
PBK attenuates paclitaxel-induced autophagic cell death by suppressing p53 in H460 non-small-cell lung cancer cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2020 May;10(5):937-950. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12855. Epub 2020 Apr 14. FEBS Open Bio. 2020. PMID: 32237067 Free PMC article.
-
G226, a novel epipolythiodioxopiperazine derivative, induces autophagy and caspase-dependent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells in vitro.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Aug;35(8):1055-64. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.47. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 25066322 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy levels are elevated in barrett's esophagus and promote cell survival from acid and oxidative stress.Mol Carcinog. 2016 Nov;55(11):1526-1541. doi: 10.1002/mc.22406. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Mol Carcinog. 2016. PMID: 26373456 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroquine potentiates the anti-cancer effect of lidamycin on non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 May;35(5):645-52. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.3. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 24727941 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

