Knowledge discovery in variant databases using inductive logic programming
- PMID: 23589683
- PMCID: PMC3615990
- DOI: 10.4137/BBI.S11184
Knowledge discovery in variant databases using inductive logic programming
Abstract
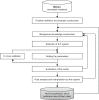
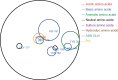
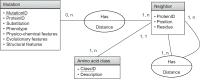
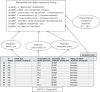
Understanding the effects of genetic variation on the phenotype of an individual is a major goal of biomedical research, especially for the development of diagnostics and effective therapeutic solutions. In this work, we describe the use of a recent knowledge discovery from database (KDD) approach using inductive logic programming (ILP) to automatically extract knowledge about human monogenic diseases. We extracted background knowledge from MSV3d, a database of all human missense variants mapped to 3D protein structure. In this study, we identified 8,117 mutations in 805 proteins with known three-dimensional structures that were known to be involved in human monogenic disease. Our results help to improve our understanding of the relationships between structural, functional or evolutionary features and deleterious mutations. Our inferred rules can also be applied to predict the impact of any single amino acid replacement on the function of a protein. The interpretable rules are available at http://decrypthon.igbmc.fr/kd4v/.
Keywords: SNP prediction; genotype-phenotype relation; human monogenic disease; inductive logic programming.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KD4v: Comprehensible Knowledge Discovery System for Missense Variant.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(Web Server issue):W71-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks474. Epub 2012 May 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22641855 Free PMC article.
-
MSV3d: database of human MisSense Variants mapped to 3D protein structure.Database (Oxford). 2012 Apr 3;2012:bas018. doi: 10.1093/database/bas018. Print 2012. Database (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 22491796 Free PMC article.
-
SM2PH-db: an interactive system for the integrated analysis of phenotypic consequences of missense mutations in proteins involved in human genetic diseases.Hum Mutat. 2010 Feb;31(2):127-35. doi: 10.1002/humu.21155. Hum Mutat. 2010. PMID: 19921752
-
Knowledge discovery in traditional Chinese medicine: state of the art and perspectives.Artif Intell Med. 2006 Nov;38(3):219-36. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2006.07.005. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Artif Intell Med. 2006. PMID: 16930966 Review.
-
Mapping genetic variations to three-dimensional protein structures to enhance variant interpretation: a proposed framework.Genome Med. 2017 Dec 18;9(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13073-017-0509-y. Genome Med. 2017. PMID: 29254494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chasman D, Adams RM. Predicting the functional consequences of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms: structure-based assessment of amino acid variation. J Mol Biol. 2001;307(2):683–706. - PubMed
-
- Thusberg J, Olatubosun A, Vihinen M. Performance of mutation pathogenicity prediction methods on missense variants. Hum Mutat. 2011;32(4):358–68. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

