Reversibility of structural and functional damage in a model of advanced diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 23641056
- PMCID: PMC3699819
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012050445
Reversibility of structural and functional damage in a model of advanced diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
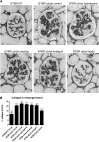
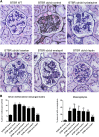
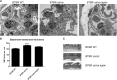
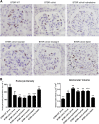
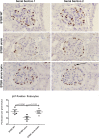
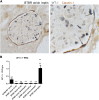
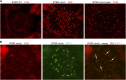
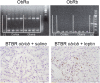
The reversibility of diabetic nephropathy remains controversial. Here, we tested whether replacing leptin could reverse the advanced diabetic nephropathy modeled by the leptin-deficient BTBR ob/ob mouse. Leptin replacement, but not inhibition of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), resulted in near-complete reversal of both structural (mesangial matrix expansion, mesangiolysis, basement membrane thickening, podocyte loss) and functional (proteinuria, accumulation of reactive oxygen species) measures of advanced diabetic nephropathy. Immunohistochemical labeling with the podocyte markers Wilms tumor 1 and p57 identified parietal epithelial cells as a possible source of regenerating podocytes. Thus, the leptin-deficient BTBR ob/ob mouse provides a model of advanced but reversible diabetic nephropathy for further study. These results also suggest that restoration of lost podocytes is possible but is not induced by RAAS inhibition, possibly explaining the limited efficacy of RAAS inhibitors in promoting repair of diabetic nephropathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beneficial effect on podocyte number in experimental diabetic nephropathy resulting from combined atrasentan and RAAS inhibition therapy.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 May 1;318(5):F1295-F1305. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00498.2019. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32249614
-
Regression of diabetic nephropathy by treatment with empagliflozin in BTBR ob/ob mice.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022 Apr 25;37(5):847-859. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfab330. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022. PMID: 34865099
-
Reversal of hypertriglyceridemia in diabetic BTBR ob/ob mice does not prevent nephropathy.Lab Invest. 2021 Jul;101(7):935-941. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00592-8. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Lab Invest. 2021. PMID: 33911188 Free PMC article.
-
The podocyte: a potential therapeutic _target in diabetic nephropathy?Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(26):2713-20. doi: 10.2174/138161207781662957. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17897015 Review.
-
Mouse models of diabetic nephropathy.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011 May;20(3):278-84. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3283451901. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 21422926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mannan-Binding Lectin Is Associated with Inflammation and Kidney Damage in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 29;25(13):7204. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137204. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000309 Free PMC article.
-
Whole transcriptome mapping reveals the lncRNA regulatory network of TFP5 treatment in diabetic nephropathy.Genes Genomics. 2024 May;46(5):621-635. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01504-y. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38536617
-
Podocytes from hypertensive and obese mice acquire an inflammatory, senescent, and aged phenotype.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Apr 1;326(4):F644-F660. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00417.2023. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38420674 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Analysis of Obesity-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy in BTBR Mice.Diabetes. 2024 Feb 1;73(2):312-317. doi: 10.2337/db23-0444. Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 37935024
-
The crosstalk between glomerular endothelial cells and podocytes controls their responses to metabolic stimuli in diabetic nephropathy.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 20;13(1):17985. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45139-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37863933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US Renal Data System: USRDS 2009 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, The National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2009.
-
- US Renal Data System: 2007 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, 2007, pp 239–254
-
- Atkins RC, Zimmet P: Diabetic kidney disease: Act now or pay later. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25: 331–333, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Reutens A, Prentice L, Atkins R: The epidemiology of diabetic kidney disease. In: The Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus, edited by Ekoe J, Chichester, Wiley, 2008
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

