ULK1 induces autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid kinase
- PMID: 23685627
- PMCID: PMC3885611
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2757
ULK1 induces autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid kinase
Abstract
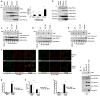
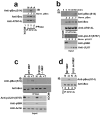
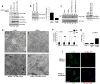
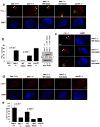
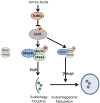
Autophagy is the primary cellular catabolic program activated in response to nutrient starvation. Initiation of autophagy, particularly by amino-acid withdrawal, requires the ULK kinases. Despite its pivotal role in autophagy initiation, little is known about the mechanisms by which ULK promotes autophagy. Here we describe a molecular mechanism linking ULK to the pro-autophagic lipid kinase VPS34. Following amino-acid starvation or mTOR inhibition, the activated ULK1 phosphorylates Beclin-1 on Ser 14, thereby enhancing the activity of the ATG14L-containing VPS34 complexes. The Beclin-1 Ser 14 phosphorylation by ULK is required for full autophagic induction in mammals and this requirement is conserved in Caenorhabditis elegans. Our study reveals a molecular link from ULK1 to activation of the autophagy-specific VPS34 complex and autophagy induction.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

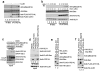
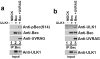
Comment in
-
Autophagy: Kinase crosstalk through beclin 1.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;14(7):402-3. doi: 10.1038/nrm3608. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23756621 No abstract available.
-
ULK1 _targets Beclin-1 in autophagy.Nat Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;15(7):727-8. doi: 10.1038/ncb2797. Nat Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23817237 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
ULK1 _targets Beclin-1 in autophagy.Nat Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;15(7):727-8. doi: 10.1038/ncb2797. Nat Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23817237 Free PMC article.
-
Cul3-KLHL20 Ubiquitin Ligase Governs the Turnover of ULK1 and VPS34 Complexes to Control Autophagy Termination.Mol Cell. 2016 Jan 7;61(1):84-97. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26687681
-
The ULK1 complex mediates MTORC1 signaling to the autophagy initiation machinery via binding and phosphorylating ATG14.Autophagy. 2016;12(3):547-64. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1140293. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 27046250 Free PMC article.
-
So Many Roads: the Multifaceted Regulation of Autophagy Induction.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Oct 15;38(21):e00303-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00303-18. Print 2018 Nov 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30126896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy regulation by nutrient signaling.Cell Res. 2014 Jan;24(1):42-57. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.166. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24343578 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy, an accomplice or antagonist of drug resistance in HCC?Cell Death Dis. 2021 Mar 12;12(3):266. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03553-7. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33712559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylation of Beclin 1 inhibits autophagosome maturation and promotes tumour growth.Nat Commun. 2015 May 26;6:7215. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8215. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26008601 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy induction by histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibits HIV type 1.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):5028-5040. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.605428. Epub 2014 Dec 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25540204 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mitochondrial outer-membrane E3 ligase MUL1 ubiquitinates ULK1 and regulates selenite-induced mitophagy.Autophagy. 2015;11(8):1216-29. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1017180. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 26018823 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Mechanisms Governing the Autophagy-Initiating VPS34 Complex and Its inhibitors.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024 Nov 1;32(6):723-735. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.094. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 39370737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011;147:728–741. - PubMed
-
- Young AR, et al. Starvation and ULK1-dependent cycling of mammalian Atg9 between the TGN and endosomes. Journal of cell science. 2006;119:3888–3900. - PubMed
-
- Backer JM. The regulation and function of Class III PI3Ks: novel roles for Vps34. Biochem J. 2008;410:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

