Contribution of epithelial innate immunity to systemic protection afforded by prolyl hydroxylase inhibition in murine colitis
- PMID: 23695513
- PMCID: PMC3772994
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2013.29
Contribution of epithelial innate immunity to systemic protection afforded by prolyl hydroxylase inhibition in murine colitis
Abstract
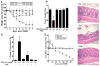
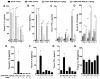
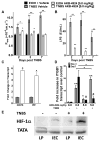
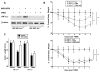
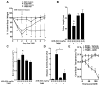
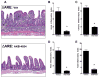
Pharmacological stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) through prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) inhibition limits mucosal damage associated with models of murine colitis. However, little is known about how PHD inhibitors (PHDi) influence systemic immune function during mucosal inflammation or the relative importance of immunological changes to mucosal protection. We hypothesized that PHDi enhances systemic innate immune responses to colitis-associated bacteremia. Mice with colitis induced by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid were treated with AKB-4924, a new HIF-1 isoform-predominant PHDi, and clinical, immunological, and biochemical endpoints were assessed. Administration of AKB-4924 led to significantly reduced weight loss and disease activity compared with vehicle controls. Treated groups were pyrexic but did not become subsequently hypothermic. PHDi treatment augmented epithelial barrier function and led to an approximately 50-fold reduction in serum endotoxin during colitis. AKB-4924 also decreased cytokines involved in pyrogenesis and hypothermia, significantly reducing serum levels of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α while increasing IL-10. Treatment offered no protection against colitis in epithelial-specific HIF-1α-deficient mice, strongly implicating epithelial HIF-1α as the tissue _target for AKB-4924-mediated protection. Taken together, these results indicate that inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase with AKB-4924 enhances innate immunity and identifies that the epithelium is a central site of inflammatory protection afforded by PHDi in murine colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflicts in the work submitted here.
Figures
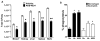
Similar articles
-
Oral delivery of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor: AKB-4924 promotes localized mucosal healing in a mouse model of colitis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015 Feb;21(2):267-75. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000277. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015. PMID: 25545377
-
Pharmacological HIF-1 stabilization promotes intestinal epithelial healing through regulation of α-integrin expression and function.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;320(4):G420-G438. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00192.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33470153
-
Local Stabilization of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Controls Intestinal Inflammation via Enhanced Gut Barrier Function and Immune Regulation.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 14;11:609689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.609689. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33519819 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors: a New Opportunity in Renal and Myocardial Protection.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022 Dec;36(6):1187-1196. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07257-0. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022. PMID: 34533692 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl 4-hydroxylase inhibition in cardiometabolic diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Dec;114:265-273. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.003. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27832958 Review.
Cited by
-
Interrelation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1 α) and the Ratio between the Mean Corpuscular Volume/Lymphocytes (MCVL) and the Cumulative Inflammatory Index (IIC) in Ulcerative Colitis.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 24;11(12):3137. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123137. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137357 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factors: a central link between inflammation and cancer.J Clin Invest. 2016 Oct 3;126(10):3689-3698. doi: 10.1172/JCI84430. Epub 2016 Aug 15. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27525434 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a critical transcription factor for IL-10-producing B cells in autoimmune disease.Nat Commun. 2018 Jan 17;9(1):251. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02683-x. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29343683 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immunity and inflammation by hypoxia in immunological niches.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Dec;17(12):774-785. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.103. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28972206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF-α Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors and Their Implications for Biomedicine: A Comprehensive Review.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 24;9(5):468. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050468. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33923349 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Karrasch T, Jobin C. Wound healing responses at the gastrointestinal epithelium: a close look at novel regulatory factors and investigative approaches. Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie. 2009;47(12):1221–1229. - PubMed
-
- Lawrance IC, Radford-Smith GL, Bampton PA, Andrews JM, Tan PK, Croft A, et al. Serious infections in patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving anti-tumor-necrosis-factor-alpha therapy: an Australian and New Zealand experience. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25(11):1732–1738. - PubMed
-
- Pastor Rojo O, Lopez San Roman A, Albeniz Arbizu E, de la Hera Martinez A, Ripoll Sevillano E, Albillos Martinez A. Serum lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in endotoxemic patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007;13(3):269–277. - PubMed
-
- Ward JB, Lawler K, Amu S, Taylor CT, Fallon PG, Keely SJ. Hydroxylase inhibition attenuates colonic epithelial secretory function and ameliorates experimental diarrhea. FASEB J. 2011;25(2):535–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

