Attenuation of dexamethasone-induced cell death in multiple myeloma is mediated by miR-125b expression
- PMID: 23759586
- PMCID: PMC3737316
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.25251
Attenuation of dexamethasone-induced cell death in multiple myeloma is mediated by miR-125b expression
Abstract
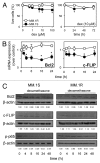
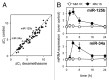
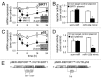
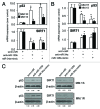
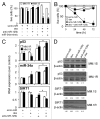
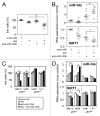
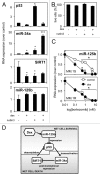
Dexamethasone is a key front-line chemotherapeutic for B-cell malignant multiple myeloma (MM). Dexamethasone modulates MM cell survival signaling but fails to induce marked cytotoxicity when used as a monotherapy. We demonstrate here the mechanism behind this insufficient responsiveness of MM cells toward dexamethasone, revealing in MM a dramatic anti-apoptotic role for microRNA (miRNA)-125b in the insensitivity toward dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. MM cells responding to dexamethasone exhibited enhanced expression of oncogenic miR-125b. Dexamethasone also induced expression of miR-34a, which acts to suppress SIRT1 deacetylase, and thus allows maintained acetylation and inactivation of p53. p53 mRNA is also suppressed by miR-125b _targeting. Reporter assays showed that both these dexamethasone-induced miRNAs act downstream of their _target genes to prevent p53 tumor suppressor actions and, ultimately, resist cytotoxic responses in MM. Use of antisense miR-125b transcripts enhanced expression of pro-apoptotic p53, repressed expression of anti-apoptotic SIRT1 and, importantly, significantly enhanced dexamethasone-induced cell death responses in MM. Pharmacological manipulations showed that the key regulation enabling complete dexamethasone sensitivity in MM cells lies with miR-125b. In summary, dexamethasone-induced miR-125b induces cell death resistance mechanisms in MM cells via the p53/miR-34a/SIRT1 signaling network and provides these cells with an enhanced level of resistance to cytotoxic chemotherapeutics. Clearly, such anti-apoptotic mechanisms will need to be overcome to more effectively treat nascent, refractory and relapsed MM patients. These mechanisms provide insight into the role of miRNA regulation of apoptosis and their promotion of MM cell proliferative mechanisms.
Keywords: NFκB; SIRT1; mir-125b; mir-34a; p53.
Figures
Similar articles
-
5-Aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonodynamic therapy induces anti-tumor effects in malignant melanoma via p53-miR-34a-Sirt1 axis.J Dermatol Sci. 2015 Aug;79(2):155-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 May 1. J Dermatol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25982144
-
miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 is suppressed by ursodeoxycholic acid in the rat liver and activated by disease severity in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Hepatol. 2013 Jan;58(1):119-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.08.008. Epub 2012 Aug 15. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 22902550
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1/c-Jun activation of the p53/microRNA 34a/sirtuin 1 pathway contributes to apoptosis induced by deoxycholic acid in rat liver.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;34(6):1100-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00420-13. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24421392 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling miRNA regulation in cancer signaling systems: miR-34a regulation of the p53/Sirt1 signaling module.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;880:87-108. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-833-7_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23361983 Review.
-
Role of tumor suppressor p53 and micro-RNA interplay in multiple myeloma pathogenesis.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Oct 26;10(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0538-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29073933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EZH2 inhibition in multiple myeloma downregulates myeloma associated oncogenes and upregulates microRNAs with potential tumor suppressor functions.Onco_target. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):10213-10224. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.14378. Onco_target. 2017. PMID: 28052011 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of p53 Deregulation in Cancer: An Overview in Multiple Myeloma.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 30;17(12):2003. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122003. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27916892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-125b: association with disease activity and the treatment response of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Jun 2;18(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1023-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27255643 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of MicroRNA deregulation on pre-RNA processing network in multiple myeloma.Leukemia. 2020 Jan;34(1):167-179. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0498-5. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Leukemia. 2020. PMID: 31182781 Free PMC article.
-
DNA hypermethylation of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) caused by betel quid chewing-a possible predictive biomarker for malignant transformation.Clin Epigenetics. 2020 Jan 13;12(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0806-y. Clin Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 31931863 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
