AKT-independent PI3-K signaling in cancer - emerging role for SGK3
- PMID: 24009430
- PMCID: PMC3762672
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S35178
AKT-independent PI3-K signaling in cancer - emerging role for SGK3
Abstract
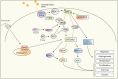
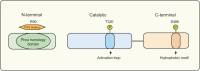
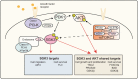
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3-K) signaling pathway plays an important role in a wide variety of fundamental cellular processes, largely mediated via protein kinase B/v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog (PKB/AKT) signaling. Given the crucial role of PI3-K/AKT signaling in regulating processes such as cell growth, proliferation, and survival, it is not surprising that components of this pathway are frequently dysregulated in cancer, making the AKT kinase family members important therapeutic _targets. The large number of clinical trials currently evaluating PI3-K pathway inhibitors as a therapeutic strategy further emphasizes this. The serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible protein kinase (SGK) family is made up of three isoforms, SGK1, 2, and 3, that are PI3-K-dependent, serine/threonine kinases, with similar substrate specificity to AKT. Consequently, the SGK family also regulates similar cell processes to the AKT kinases, including cell proliferation and survival. Importantly, there is emerging evidence demonstrating that SGK3 plays a critical role in AKT-independent oncogenic signaling. This review will focus on the role of SGK3 as a key effector of AKT-independent PI3-K oncogenic signaling.
Keywords: AKT; PI3-kinase; SGK3; cancer; mTOR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Follicle-Stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates phosphorylation and activation of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) and serum and glucocorticoid-lnduced kinase (Sgk): evidence for A kinase-independent signaling by FSH in granulosa cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Aug;14(8):1283-300. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.8.0500. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10935551
-
Regulation of KCNE1-dependent K(+) current by the serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) isoforms.Pflugers Arch. 2003 Feb;445(5):601-6. doi: 10.1007/s00424-002-0982-y. Epub 2002 Dec 4. Pflugers Arch. 2003. PMID: 12634932
-
Design and Characterization of SGK3-PROTAC1, an Isoform Specific SGK3 Kinase PROTAC Degrader.ACS Chem Biol. 2019 Sep 20;14(9):2024-2034. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00505. Epub 2019 Sep 5. ACS Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31461270 Free PMC article.
-
Serum and glucocorticoid inducible protein kinases (SGKs): a potential _target for cancer intervention.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 Sep;8(5):767-771. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 30245963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling: impaired on/off switches in aging, cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease.Exp Gerontol. 2013 Jul;48(7):647-53. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.02.025. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Exp Gerontol. 2013. PMID: 23470275 Review.
Cited by
-
Prolonged inhibition of class I PI3K promotes liver cancer stem cell expansion by augmenting SGK3/GSK-3β/β-catenin signalling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 25;37(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0801-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29940988 Free PMC article.
-
The role of non-coding RNAs in chemotherapy for gastrointestinal cancers.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Oct 8;26:892-926. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.004. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34760336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
INPP4B promotes cell survival via SGK3 activation in NPM1-mutated leukemia.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jan 17;37(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0675-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29343273 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Expression of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase p110α and Gene Amplification of PIK3CA in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2016 Apr;22(2):413-9. doi: 10.1007/s12253-015-0007-8. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Pathol Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 26581613
-
Loss of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 3 (SGK3) does not affect proliferation and survival of multiple myeloma cell lines.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 2;10(4):e0122689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122689. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25837824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sheppard K, Kinross KM, Solomon B, Pearson RB, Phillips WA. _targeting PI3 kinase/AKT/mTOR signaling in cancer. Crit Rev Oncog. 2012;17(1):69–95. - PubMed
-
- De Luca A, Maiello MR, D’Alessio A, Pergameno M, Normanno N. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT signalling pathways: role in cancer pathogenesis and implications for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2012;16(Suppl 2):S17–S27. - PubMed
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Stephens L, Hawkins P. PI3K signalling: the path to discovery and understanding. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(3):195–203. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA. _targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(8):550–562. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

